- Home
- Competitive Exam Notification & Syllabus, IAS, PCS, SSC, RRB
Competitive Exams Notification & Syllabus
The Syllabi and Notifications of UPSC & State PSCs, SSC, RRB, Bank and other Competitive Exams are available here.
Group-1
Paper-1 (Preliminary)
General studies
Marks: 120, Question: 120, Time: 120 Minutes
- Indus Valley Civilization: Features, Sites, Society, Cultural History, Art and Religion. Vedic Age- Mahajanapadas, Religions-Jainism and Buddhism.
The Maghadas, the Mauryan, Foreign invasions on India and their impact the Kushans. The Sathavahanas the Sangam Age, the Sungas, the Gupta Empire – their Administration Social, Religious and Economic Conditions-Art, Architecture, Literature, Science and Technology. - The Kanauj and their Contributions, South Indian Dynasties – The Badami Chalukyas, the Eastern Chalukyas, the Rastrakutas, the Kalyani Chalukyas, the Cholas, the Hoyasalas, the Yedavas, the Kakatiyas and the Reddis.
- The Delhi Sultannate, the Vijaynagar Empire and the Mughal Empire, the Bhakti Movement and Sufism – Administration, Economy, Society, Religion, Literature, Arts and Architecture.
- The European Trading Companies in India – their struggle for supremacy with special reference to Bengal, Bombay, Madras, Mysore, Andhra and Nizam, Governor-Generals and Viceroys.
- Indian War of Independence of 1857 – Origin, Nature, causes, consequences and significance with special reference to Concerned State, Religious and Social Reform Movements in 19th century in India and Concerned State, India's Freedom Movement, Revolutionaries in India and Abroad.
- Mahatma Gandhi, his thoughts, Principles and Philosophy. Important Satyagrahas, the Role of Sardar Patel, Subash Chandrabose in Freedom Movement and Post independence consolidation.
Dr. B.R. Ambedkar, his life and contribution to making of Indian Constitution, Indian After Independence Reorganization of the States in India.
(B) CONSTITUTION, POLITY, SOCIAL JUSTICE AND INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS.
- Indian Constitution: Evolution, features, Preamble, Fundamental Rights, Fundamental Duties, Directive Principles of State Policy, Amendments, Significant Provisions and Basic Structure.
- Functions and Responsibilities of the Union and the States, parliament and state Legislatures: Structure, Function, Power and Privileges, Issues and challenges pertaining to Federal Structure: Devolution of Power and Finances up to local levels and challenges therein.
- Constitutional Authorities: Powers, Functions and Responsibilities – Panchayati Raj – Public Policy and Governance.
- Impact of Liberalization, Privatization and Globalization on Governance – Statutory, Regulatory and Quasi-judicial bodies.
- Rights Issues (Human rights, Women rights, SC/ST rights, Child rights) etc.
- India's Foreign Policy – International Relations – Important Institutions, Agencies and Fora, their structure and mandate – Important Policies and Programmes of Central and State Governments.
(C) INDIAN AND ANDHRA PRADESH ECONOMY AND PLANNING
- Basic characteristics of Indian Economy as a developing economy – Economic development since independence objectives and achievements of planning – NITI Ayog and its approach to economic development Growth and distributive justice – Economic development Human Development Index – India's rank in the world – Environmental degradation and challenges – Sustainable Development – Environmental Policy
- National Income and its concepts and components – India's National Accounts – Demographic issues – Poverty and Inequalities – Occupational Structure and Unemployment – Various Schemes of employment and poverty eradication – Issues of Rural Development and Urban Development.
- Indian Agriculture – Irrigation and water – Inputs of agriculture – Agricultural Strategy and Agricultural Policy – Agrarian Crisis and land reforms – Agricultural credit – Minimum Support prices – Malnutrition and Food Security – Indian Industry – Industrial policy – Make-in India – Start-up and Stand-up programmes – SEZs and Industrial Corridors – Energy and Power policies – Economic reforms – Liberalisation, Privatisation and Globalization – International Trade and Balance of Payments – India and WTO.
- Financial Institutions – RBI and Monetary Policy – Banking and Financial Sector Reforms Commercial Banks and NPAs – Financial Markets – Instabilities – Stock Exchanges and SEBI – Indian Tax System and Recent changes – GST and its impact on commerce and Industry – Centre, States financial relations – Financial Commissions – Sharing of resources and devolution – Public Debt and Public Expenditure – Fiscal Policy and Budget
-
- The characteristics/basic features of Andhra Pradesh economy after bifurcation in 2014 – Impact of bifurcation on the endowment of natural resources and state revenue – disputes of river water sharing and their impact on irrigation- new challenges to industry and commerce the new initiatives to develop infrastructure- power and transport- information technology and e-governance – Approaches to development and initiatives in agriculture, industry and social sector – Urbanisation and smart cities – Skill development and employment – Social welfare programmes
- (A.P. Reorganisation Act, 2014 – Economic Issues arising out of bifurcation- Central government's assistance for building a new capital, compensation for loss of revenue, development of backward districts – Issues such as Vizag railway zone, kadapa steel factory, Dugarajapatnam airport, Express ways and industrial corridors etc., - Special Status and Special Assistance Controversy – Government's stand and measure.
(D) GEOGRAPHY
- General Geography: Earth in Solar system, Motion of the Earth, Concept of time, Season, Internal Structure of the Earth, Major landforms and their features. Atmosphere-structure and composition, elements and factors of Climate, Airmasses and Fronts, atmospheric disturbances, climate change.
Oceans: Physical, Chemical and biological characteristics, Hydrological Disasters, Marine and Continental resources. - Physical: World, India and concerned State: Major physical divisions, Earthquakes, landslides, Natural drainage, climatic changes and regions, Monsoon, Natural vegetation, Parks and Sanctuaries, Major Soil types, Rocks and Minerals.
- Social: World, India and concerned State: distribution, density, growth, Sex-ratio, Literacy, Occupational Structure, SC and ST Population, Rural-Urban components, Racial, tribal, religious and linguistic groups, urbanization, migration and metropolitan regions.
- Economic: World, India and concerned State: Major sectors of economy, Agriculture, Industry and Services, their salient features. Basic Industries-Agro, mineral, forest, fuel and manpower based Industries, Transport and Trade, Pattern and Issues.
Paper-II
General Aptitude
Marks: 120, Question: 120, Time: 120 Minutes
A. GENERAL MENTAL AND PSYCOLOGICAL ABILITIES
- Logical Reasoning and Analytical Ability.
- Number Series, Coding – Decoding.
- Problems Related to Relations.
- Shapes and their Sub-sections, Venn Diagram.
- Problems based on Clocks, Calendar and Age.
- Number system and order of Magnitude.
- Ratio, proportion and variation.
- Central Tendencies – mean, median, mode – including weighted mean.
- Power and exponent, Square, Square Root, Cube Root, H.C.F. and L.C.M.
- Percentage, Simple and Compound Interest, Profit and loss.
- Time and Work, Time and Distance, Speed and Distance.
- Area and Perimeter of Simple Geometrical Shapes, Volume and Surface Area of Sphere, Cone, Cylinder, cubes and Cuboids.
- Lines, angels and common geometrical figures – properties of transverse and parallel lines, properties of triangles, quadrilateral, rectangle, parallelograme and rhombus.
- Introduction to algebra – BODMAS, simplification of weird symbols.
- Data interpretation, Data Analysis, Data sufficiency and concepts of probability.
- Emotional Intelligence: Understanding and analyzing emotions, Dimensions of emotional intelligence, coping with emotions, empathy and coping with stress.
- Social Intelligence, interpersonal skills, Decision making, Critical thinking, problem solving and Assessment of personality.
(B) SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY - Science and Technology: Nature and Scope of Science and Technology; Relevance of Science and Technology to the day to day life; National Policy on Science, Technology and Innovation; Institutes and Organization in India promoting integration of Science, Technology and Innovation, their activities and contribution; Contribution of Prominent Indian Scientists.
- Information and Communication Technology (ICT): Nature and Scope of ICT; ICT in day to day life; ICT and Industry; ICT and Governance – various government schemes promoting use of ICT, E-Governance programmes and services; Netiquettes; Cyber Security Concerns – National Cyber Crime Policy.
- Technology in Space & Defence: Evolution of Indian Space Programme; Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) – it's activities and achievements; Various Satellite Programmes – Satellites for Telecommunication, Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS), Indian Remote Sensing (IRS) Satellites; Satellites for defence, Eduset or Satellites for academic purposes; Defence Research and Development Organization (DRDO) – vision, mission and activities.
- Energy Requirement and Efficiency: India's existing energy needs and deficit; India's Energy Resources and Dependence, Energy policy of India Government Policies and Programmes. Solar, Wind and Nuclear energy
- Environmental Science: Issues and concerns related to environment; Its legal aspects, policies and treaties for the protection of environment at the national and the international level; Biodiversity its importance and concerns; Climate change, International Initiatives (Policies, Protocols) and India's commitment; Forest and Wildlife- Legal framework for Forest and Wildlife Conservation in India; Environmental Hazards, pollution, carbon emission, Global warming. National Action plans on Climate Change and Disaster management. Biotechnology and Nanotechnology; Nature, scope and application, Ethical, Social and Legal issues, Government Policies. Genetic Engineering; Issues related to it and its impact on human life. Health & Environment.
C. CURRENT EVENTS OF REGIONAL, NATIONAL AND INTERNATIONAL IMPORTANCE.
APPSC GROUP -1 MAINS
GROUP -1 English (Mains)
Marks: 150, Time: 150 Minutes
1.ESSAY (A minimum of 200 words and a maximum of 250 words): 20 Marks
Choose any one topic from a list of five. (Descriptive/analytical/Philosophical/based on Current Affairs)
2.LETTER WRITING (in about 100 words): 10 Marks
A formal letter expressing one's opinion about in issue. The issues can deal with daily office matters/a problem that has occurred in the office/an opinion in response to one sought by a ranked officer etc.
3.PRESS RELEASE/APPEAL (in about 100 words): 10 Marks
The PR or appeal should be on an issue pertaining to a recent concern/problem/ disaster/rumours etc.
4.REPORT WRITING (in about 150 words): 15 Marks
A report on an official function/event/field trip/survey etc.
5.WRITING ON VISUAL INFORMATION (in about 150 words): 15 Marks
A report on a graph/image/flow chart/table of comparison/simple statistical data etc.
6.FORMAL SPEECH (in about 150 words): 15 Marks
A speech (in formal style) that is to be read out in a formal function. This could be an inauguration speech, an educational seminar/conference, a formal ceremony of importance etc.
7.PRECIS WRITING: 15 Marks
A precis in about 100 words for a 300-word passage.
8.READING COMPREHENSION: 15 Marks
A reading passage of about 250 words to be given followed by short-answer type questions.
9.ENGLISH GRAMMAR: 20 Marks
Multiple choice questions set from the following list:
a.Tenses
b.Voice
c.Narration (Direct-indirect)
d.Transformation of sentences
e.Use of Articles and Determiners
f.Use of Prepositions
g.Use of Phrasal Verbs
h.Use of idiomatic expressions
i.Administrative Glossary
j.Synonyms/Antonyms
k.One-word substitution
l.Cohesive devices/Connectives/Linkers
m.Affixes
n.Words that cause confusion like hononyms/homophones.
10.TRANSLATION: 15 Marks
Translation of a short passage (of about 150 words)
From Regional language to English.
GROUP-1Telugu (Mains)
Marks: 150Time: 150 Minutes
1.Essay (A minimum of 200 words and a maximum of 250 words): Choose any one topic from a list of five. (Descriptive/analytical/losophical/based on Current Affairs)20
2.To ELABORATE the thought of poetic or verse (any two of the three) (about 100 words)10
3.PRECIS WRITING : 1/3rd summary of the given passage in your words10
4.COMPREHENTION : A reading passage of about 250 words to be given followed by short answer type questions.10
5.FORMAL SPEECH (Welcome, Farewell, Inauguration etc.) / Speech for the press conference (energy, farm credit, pollution, health related policy or problem) (in about 150 words)10
6.To PREPARE THE STATEMENTS for publicity media (in about 100 words)10
7.LETTER WRITING (in about 100 words): Congratulation/ Best wishes/Request/ Complaint etc.)10
8.DEBATE WRITING (in about 150 words) (Newspaper issues/current issues/editorial presenting individual opinion) 10
9.APPLICATION WRITING (in about 150 words)10
10.RRPORT WRITING (in about 150 words)10
11.DIALOGUE WRITING ORDIALOGUE SKILLS : Dialogues between two people (in about 150 words) (Group discussion, work of the meeting, water, agriculture, health, sanitation, education related problems etc.)10
12.TRANLATION: Translation from English to Telugu Language10
13.Grammar of Telugu20
Total150
General Essay (Paper-I)
Marks: 150, Time: 150 Minutes
The candidates are required to attempt three essays, one from each of the three sections in about 800 words each.
Objective:
This paper is designed to test candidate's (i) knowledge/awareness of a variety of Subjects and (ii) their ability to compose a sustained piece of writing in the form of an essay.
Contents:
i. Current affairs
ii. Socio-political issues
iii. Socio economic issues
iv.Socio-environmental issues
v.Cultural and historical aspects
vi.Issues related to civic awareness
vii.Reflective topics
Areas of Testing:
This paper would test the following:
1.Ability to compose a well-argued piece of writing
2.Ability to express coherently and sequentially
3.Awareness of the subject chosen
Evaluation/Marking:
Credit will be given for the following:
a.Observing established rules and format for essay writing
b. Grammatical correctness of expression
c.Originality of thought and expression.
General Essay (Paper-I)
Marks: 150Time: 150 Minutes
History, Culture and Geography of India and Andhra Pradesh
A.History and Culture of India
1.Pre-Historic Cultures in India-Indus Valley Civilization Vedic Culture- Mahajanapadas Emergence of New Religions-Jainism, Buddhism- Rise of the Magadha and Age of the Mauryas Ashoka Dharma-Foreign Invasions on India- The Kushans.
The Satavahanas, the Sangam Age in South India- the Sungas- the Guptas- the Kanauj and their Contributions- Historical Accounts of Foreign travelers- Early Educational Institutions.
2.The Pallavas, the Badami Chalukyas, the Eastern Chalukyas, the Rashtrakutas, the Kalyani Chalukyas and the Cholas- Socio Cultural Contributions, Language, Literature Art and Architecture – Delhi Sultanates- Advent of Islam and its Impact- Religious Movements like Bhakti and Sufi and Its Influence.
Growth of Vernacular Languages, Scripts, Literature, Fine Arts- Socio Cultural Conditions of the Kakatiyas, the Vijayanagaras, the Bahmanis, the Qutubsahis and their cotemporary South Indian kingdoms.
3.The Mughals Administration, Socio-Religious life and Cultural developments- Shivaji and Rise of Maratha Empire- Advent of Europeans in India.
Trade practices- Rise of East India Company its Hegemony- Changes in Administration, Social and Cultural spheres- Role of Christian Missionaries.
4.Rise of British rule in India from 1757to 1856- Land Revenue Settlement, Permanent Settlement, Ryothvari and Mahalvari- 1857 Revolt and its Impact-Education, Press, Cultural changes- Rise of National Consciousness and Changes- Socio-Religious Reform Movements in 19th century- Rajaram Mohan Roy, Dayananda Saraswathi, Swamy Vivekananda, Annie Besant, Sir Syed Ahmad Khan and others.
Rise of India Nationalism- Activities of Indian National Congress- Vandemataram, Home Rule Movements- Self Respect Movement- Jyothiba Phule, Narayana Guru, Periyar Ramaswamy Naicker- Role of Mahatma Gandhi, Subhash Chandra Bose, Vallabai Patel- Satyagraha- Quit India Movement- Dr B. R. Ambedkar and his Contributions.
5.Indian Nationalism in three phases-Freedom Struggle 1885-1905, 1905-1920 and Gandhi Phase 1920-1947- Peasant, Women, Tribal and Workers Movements- Role of Different Parties in Freedom Struggle- Local and Regional Movements- Inter Religious Unity and Communalism.
Independence and partition of India- India after Independence- Rehabilitation after partition Linguistic Re-organization of States Integration of the Indian States- Indian Constitution Economic policies- Foreign Policy Initiatives.
B.History and Culture of Andhra Pradesh
6.Ancient: The Satavahanas, the Ikshvakus, the Salankayanas, the Pallavas and the Vishnukundins- Social and Economic Conditions Religion, Language (Telugu), Literature, Art and Architecture- Jainism and Buddhism in Andhra.
The Eastern Chalukyas, the Rashtrakutas, the Renati Cholas and others- Socio-Cultural life, Religion- Telugu Script and Language, Literature, Art and Architecture.
7.Medieval: Socio – Cultural and Religious Conditions in Andhradesa 1000 to1565 A.D. – Antiquity, Origin and Growth Telugu Language and Literature (Kavitraya – Asthadiggajas)- Fine Arts, Art & Architecture during the reign of Kakatiyas, Reddis, Gajapatis and Vijayanagaras and their feudatories.
Historical Monuments-Significance, Contribution of Qutubshahis to Andhra History and Culture Regional Literature- Praja Kavi – Vemana and others.
8.Modern: European Trade Establishments in Andhra- Andhra Under the Company Rule- Role of Christian Missionaries- Socio-Cultural, Literary Awakening- C.P. Brown, Thamos Munro, Mackenzie-Zamindary, Polegary System- Native States and Little Kings.
Role of Social Reformers – Gurajada Apparao, Kandukuri Veeresa lingam, Raghupati Venkataratnam Naidu, Gidugu Ramamurthy, Annie Besant and others- Library movement in Andhra Pradesh- Role of News Paper- Fok and Tribal Culture, Oral Traditions, Subaltern Culture, Role of women.
9.Nationalist Movement: Role of Andhra leaders- Justice Party, Non Brahmin Movement nationalist and Revolutionary Literature- Gurram Jashva, Boyi Bheemanna, Sri Sri, Garimella Satyanarayana, Rayaprolu Subbarao, Unnava Lakshminarayana, Tripuraneni Ramaswamy Choudhary and others,
Andhra Mahasabhas, Andhra Movement- prominent leaders- Alluri sitaramraju, Duggirala Gopalakrishnaiah, Konda Venkatappayya, Pattabhi Seetaramaiah, Ponaka Kanakamma, Dokka Sitamma-Grandhlaya Movement- Ayyanka Venkataratnam, Gadicherla Harisarvothamarao, Kasinanathuni Nagesvara Rao- Potti Sreeramulu Formation of Andhra State, 1953- Emergence of Andhra Pradesh, 1956- Andhra Pradesh 1956 to 2014- Causes for Bifurcation, 2nd June 2014 Impact.
10.Andhra Pradesh: Bifurcation of Andhra Pradesh and its impact on Administrative, Economic, Social, Political, Cultural and Legal Implications- Loss of Capital City, Building of New Capital and its financial Implications- Division of Employees and their Native Issues Effect of Bifurcation on Trade and Commerce, Industry – Implication of Financial Resources of State Government.
Developmental Opportunities- Socio-Economic, Cultural and Demographic impact of Bifurcation Impact on River water sharing and other link issues- Andhra Pradesh Reorganization Act. 2014 the Arbitrariness of certain provisions.
11.Physical Features and Resources: India and Andhra Pradesh, Major land forms, Climatic changes, Soil types, Rivers, Water, Streams, Geology, Rocks, Mineral Resources, Metals, Clays, Construction Materials, Reservoirs, Dams – Forests, Mountains, Hills, Flora and fauna, Plateau Forests, Hill Forests, Vegetation Classification.
12.Economic Geography: Agriculture, Live stocks, Forestry, Fishery, Quarrying, Mining, House hold Manufacturing, Industries – Agro, Mineral, Forest, Fuel and man power, Trade and Commerce, Communication, Road Transport, Storage and others.
13.Social Geography: Population Movements and Distribution, Human Habitations, Density, Age, Sex, Rural, Urban, Race, Caste, Tribe, Religion, Linguistic, Urban Migration, Education Characteristics.
14.Fauna and Floral Geography: Wild Animals, Animals, Birds, Reptiles, Mammals, Trees and Plants and others.
15.Environmental Geography: Sustainable Development, Globalization, Temperature, Humidity, Cloudiness, Winds, Special Weather Phenomena, Natural Hazards – Earth Quakes, Land Slides, Floods, Cyclones, Cloud Burst, Disaster Management, Impact Assessment, Environmental Pollution, pollution Management.
GROUP -1
Marks: 150, Time: 150 Minutes
Paper III
Polity, Constitution, Governance, Law and Ethics
(A) Indian Polity and Constitution
1.Indian Constitution and its salient features – Functions and duties of the Indian Union and the State Governments.
2.Issues and challenges pertaining to the Federal structure – Role of Governor in States – Distribution of powers between the Union and States (Union list, State list and Concurrent list) – Issues and challenges.
3.Rural and Urban Local Governance under 73rd and 74th Constitutional Amendment – Constitutional Authorities and their Role.
4.Parliament and State Legislatures – structure, functioning, conduct of business, powers and privileges and issues arising out of these.
5.Judiciary in India – Structure and functions, important provisions relating to emergency and constitutional amendments, judicial review, public Interest Litigation.
(B)Public Administration and Governance
6.Meaning, Nature and scope of Public Administration – Evolution in India – Administrative ideas in Kautilya's Arthashastra; Mughal administration; Legacy of British rule.
7.Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues and problems of implementation.
8.Development processes the role of civil society, NGOs and other stakeholders –
9.Statutory, regulatory and various quasi-judicial authorities – Role of Civil Services in Democracy.
10.Good governance and e-governance- Transparency, accountability and responsiveness in governance – Citizen's Charter. RTI, Public Service Act and their implications, Concept of Social Audit and its importance.
C.Ethics in Public Service and knowledge of law
11.Ethics and Human Interface: Essence, determinants and Consequences of Ethics in Human actions: dimensions of Ethics: Ethics in Private and Public relationships, Ethics-integrity and Accountability in Public Service.
12.Human values: Understanding the Harmony in existence Human relationships in the society and in the Nature. Gender Equability in the relationships Role of family, society and Educational Institutions in imparting values to citizens, lessons from the lives and teachings of great leaders, reformers and administrations.
13.Attitude: Content, Functions, its influence and relation with thought and behaviour, Moral and Political attitudes, role of Social influence and persuasion. Emotional intelligence Concepts and their utilities and application in Administration and Governance.
14.Concept of Public Service, "Philosophical basis of Governance professional Ethics in the light of right understanding and Vision for Holistic Technologies, Codes of Ethics, codes of Conduct, RTI, Public Service Act, Leadership Ethics, Work culture, Ethical principles with in an Organizational content. Ethical and moral values in governance, Ethical issues in international relations, corruption, Lokpal, Lokayukta
15.Basic Knowledge of Laws in India
Constitution of India: Nature and salient features – Fundamental Rights and Directive Principles of State Policy – Bifurcation of powers between centre and state (state list, union list and concurrent list) – Powers of judiciary, executive and legislature.
Civil and Criminal law: hierarchy of civil and criminal courts in India – difference between substantial and procedural laws – order and decree – new developments in criminal laws, Nirbhaya Act.
Labour Law: Concept of social welfare legislations in India, changing trends in employment and necessity for new labour laws.
Cyber Laws: Information Technology Act – Cyber Security and Cyber Crime – difficulties in determining competent jurisdiction of courts in case of cyber-crimes.
Tax Laws: Laws relating to imcome, Profits, Wealth Tax, Corporate Tax – GST
GROUP-1
Marks: 150, Time: 150 Minutes
Paper-IV
Economy and Development of India and Andhra Pradesh
1.Major Challenges of Indian Economy: Inconsistent growth rate, Low growth rates of agriculture and manufacturing sectors, inflation and oil prices, current account deficit and unfavorable balance of payments, falling rupee value, growing NPAs and capital infusion – money laundering and black money – Insufficient financial resources and deficiency of capital, lack of Inclusive growth and Sustainable development – Nature, causes, consequences and solutions of these problems
2.Resource Mobilization in Indian Economy: Sources of financial resources for public and private sectors – budgetary resources – tax revenue and non-tax revenue – public debt : market borrowings, loans and grants etc., external debt from multilateral agencies – foreign institutional investment and foreign direct investment – desirability and consequences of utilizing different sources – Monetary and fiscal policies – financial markets and institutions of developmental finance investment in industries and infrastructure projects – Physical resources – Energy resources
3.Resource mobilization in Andhra Pradesh: Budgetary resources and constraints – Fulfillment of the conditions of A.P Bifurcation Act – central assistance and issues of conflict – public debt and projects of external assistance – Physical resources – Mineral and forest resources – Water disputes with neighboring states.
4.Government Budgeting: Structure of Government budget and its components – Budgeting process and recent changes of Types of budget – types of deficits, their impact and management – Highlights of current year's union budget and its analysis GST and related issues – Central assistance to states – Issues of federal finance in India – Recommendations of the latest finance commission.
5.Government budgeting in Andhra Pradesh: Budget constraints Central assistance and issues of conflict after bifurcation of the state management of deficits – Highlights and Analysis of the current year budget – State finance commission and local finance in Andhra Pradesh.
6.Inclusive Growth: Meaning of inclusion – Causes of exclusion in India – Strategies for and instruments of inclusion: Poverty alleviation and employment, Health and Education, women empowerment, social welfare schemes – Food Security and Public Distribution System – sustainable agriculture – Integrated Rural development – regional diversification – Public and partnership for inclusive growth – Financial inclusion
All Andhra Pradesh government's current schemes for inclusive growth and financial inclusion – Public Distribution system and DWCRA
7.Agricultural Development: Role of agriculture in economic development – Contribution of to GDP – Issues of finance, production, marketing – green revolution and changing focus to dryland farming, organic farming and sustainable agriculture minimum support prices – agriculture policy – Swaminathan Commission – Rainbow revolution –
8.Agriculture Development in Andhra Pradesh: Contribution to SGDP-Regional disparities in irrigation and agricultural development changing cropping pattern – focus on horticulture and fisheries and dairying – Government schemes to promote agriculture in Andhra Pradesh
9.Industrial Development and Policy: Role of industrial sector in economic development – Evolution of industrial policy since independence – Industrial policy, 1991 and its impact on Indian economy – Contribution of Public Sector to industrial development in india – impact of liberalization and privatization and globalization on industrial development – Disinvestment and privatization – Problems of core industries – Micro, small and medium enterprises, their problems and policy – Industrial sickness and support mechanism – Manufacturing policy – Make in India – Start up programme – NIMZs – SEZs, industrial corridors –
10.Industrial Policy of the AP Government: Incentives to industries – Industrial corridors in the SEZs in Andhra Pradesh – Bottlenecks for industrial development – power projects
11.Infrastructure in India: Transport infrastructure: ports, Roads, Airports, Railways – Major projects of transport infrastructure in India – Communication infrastructure – Information Technology – e-governance – Digital India – Energy and power – Urban infrastructure – smart cities – urban environment – solid waste management – Weather forecast and disaster management – Issues of finance, ownership, operation and maintenance of all kinds of infrastructure – Public-private partnership and related issues – Pricing of public utilities and government policy – environmental impacts of infrastructure projects.
12.Infrastructure Development in Andhra Pradesh: Transport, Energy and ICT infrastructure – Bottlenecks – Government policy – Ongoing projects
GROUP-1
Marks: 150, Time: 150 Minutes
Paper-V
Science and Technology
1.Integration of Science, Technology and Innovation for better human life; Science & Technology in everyday life; National Policies on proliferation of Science, Technology and Innovation; India's contribution in the field of Science and Technology. Concerns and challenges in the proliferation and use of science and technology, Role and Scope of Science and Technology in nation building Major Scientific institutes for Science and technology in AP and India. Major Scientific Institutes for Research and Development in AP and India. Achievements of Indian Scientist in the field of Science and Technology Indigenous technologies and developing new technologies.
2.Information and Communication Technology (ICT) – its importance, advantages and challenges; E-governance and India; Cyber Crime and policies to address security concerns. Government of India Policy on Information Technology (IT). IT Development in AP and India.
3.Indian Space Programme – Past, Present and Future; Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) – it's activities and achievements; Satellite Programmes of India and Use of Satellites in different fields like Health, Education, Communication Technology, Weather forecasting affecting human lives; Defence research and Development Organization (DRDO).
4.Indian's energy needs, efficiency and resources; Clean energy resources; Energy policy of India – Government Policies and Programmes. Conventional and Non-Conventional energy resources. Energy demands, Indian Energy Sciences, Conventional energy powers, Tharmal, renewable energy resources, Solar wind, Bio and wasted based, energy policies Geotharmal and Tidel Sources, energy Policies in India, energy security.
Salient features of Nuclear Policy of India; Development of Nuclear programmes in India, Nuclear Policies at the International level and India's stand on them.
5.Development Vs. Nature / Environment; Depletion of Natural Resources Metals, Minerals – Conservation Policy. Environmental Pollution Natural and Anthropogenic and Environmental degradation. Sustainable Development – possibilities and challenges; Climate Change and its effect on the world; Climate justice – a global phenomenon; Environment Impact Assessment, Natural Disasters – Cyclones, Earth Quakes, Landslides and Tsunamis – Prediction Management. Correlation between Health & Environment, Social Forestry, Afforestation and deforestation, Mining in AP and India. Types of Natural resources renewable and Nonrenewable. Forest resources. Fishery resources. Fossil Fuels Coal, Petroleum and Natural Gas. Mineral resources. Water resources – Types, Water shed management. Land resources – types of soils and soil reclamation.
6.Environmental pollution and Solid waste management: Sources, impacts and control of air pollution, water pollution and soil pollution. Noise pollution. Solid waste management types of solid waste, impacts of solid waste, recycling and reuse, Remedial measurers for Soil erosion and Costal erosion.
Global Environmental issues and role of information Technology in Environment and Human Health, Ozone layer depletion, Acid rain. Global Warming and its impacts.
Environmental legislation: International Law, Montreal protocol, Kyoto protocol, United Nations Framework Convention on Climate change, CITES. The Environment (Protection) act 1986, Forest conservation Act, Wildlife protection act. Biodiversity Bill of India – cop 21 – Sustainable Development Goals – National Disaster Management Policy, 2016 of India and Disaster management initiatives in India.
White Revolution, Green Revolution and Green Pharmacy
7.Nature, Scope and Applications of Biotechnology and Nanotechnology in India; Ethical, Social and Legal concerns, Government policies; Genetic engineering, issues related to it and its impact on human life. Bio – diversity, fermentation, Immuno – diadnosis techniques.
8.Human diseases-microbial infections. Common infections and preventive measures. Introduction to bacterial, viral, protozoal and fungal infections. Basic knowledge of infections-diarrhoea, dysentry, cholera, tuberculosis, malaria, viral infections like HIV, Encephalitis, Chikungunya, bird flu-preventive measures during out breaks. Introduction to Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology. Basic concepts of genetic engineering. Tissue culture methods and applications, Biotechnology in agriculture- Bio-pesticides, Bio-fertilizers, Bio-fuels, Genetically modified crops. Animal husbandry-transgenic animals.
Vaccines: Introduction to immunity, Fundamental concepts in vaccination, Production of Modern Vaccines (production of Hepatitis Vaccine).
9.Issues related to Intellectural Property Rights in the field of Science and Technology. Promotion of Science in AP and India.
| SCHEME AND SYLLABUS FOR GROUP-II SERVICES | |
| PRELIMINARY & MAINS EXAMINATION PATTERN | |
| Subject | Marks |
| Screening Test | 150 |
| Main Examination | |
| Paper-I | |
| General Studies & Mental Ability | 150 |
| Paper-II | |
| I.Social History of Andhra Pradesh i.e., the history of various social and Cultural Movements in Andhra Pradesh | 150 |
| II.General overview of the Indian Constitution | 150 |
| Paper-III | |
| Planning in India and Indian Economy | |
| Contemporary problems and Developments in Rural Society with special reference to Andhra Pradesh. | 150 |
| Total = 450 | |
PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION
GROUP-II
Section – A
General Studies and Mental Ability
1.Events of national and international importance.
2.Current affairs international, national and regional.
3.General Science and its applications to the day to day life Contemporary developments in Science and Technology and Information Technology.
4.Social economic and political history of modern India with emphases on indian national movement.
5.Indian polity and governance: constitutional issues, public policy, reforms and e-governance initiatives.
6.Geography of India with focus on Andhra Pradesh.
7.Disaster management: vulnerability profile, prevention and mitigation strategies, Application of Remote Sensing and GIS in the assessment of Disaster
8.Sustainable Development and Environmental Protection
9.Logical reasoning, analytical ability and logical interpretation.
10.Data Analysis: Tabulation of data Visual representation of data Basic data analysis (Summary Statistics such as mean, median, mode and variance) and Interpretation.
11.Bifurcation of Andhra Pradesh and its Administrative, Economic, Social, Cultural, Political and legal implications/problems.
Section – B
Social and Cultural History of Andhra Pradesh
1.Social and Cultural History of Andhra Pradesh: Geographical Features of Andhra – Its Impact on History and Culture – Pre-historic Cultures – The Satavahanas, The Ikshvakus – Socio-economic and Religious Conditions – Literature, Art and Architecture – The Vishnukundins, The Eastern Chalukyas of Vengi, Telugu Cholas-Society, Religion, Telugu Language, Literature, Art and Architecture.
2.Various Major and Minor dynastices that ruled Andhradesa between 11th and 16th centuries A.D. Socio Cultural and Religious conditions in Andhradesa between 11th to 16th centuries A.D, Social structure, Caste System, Status of Women. Growth of Telugu Language, Literature, Art, Architecture and Painting.
3.Advent of Europeans- Trade centers – Andhra under the Company 1857 Revolt and its impact on Andhra Establishment of British RuleSociocultural awakening, Justice Party/Self Respect Movements Growth of Nationalist Movement in Andhra between 1885 to 1947 Role of Socialists – Communists – Anti Zamindari and Kisan Movements. Growth of Nationalist Poetry, Revolutionary Literature, Nataka Samasthalu and Women Participation.
4.Origin and growth of Andhra Movement Role of Andhra Mahasabhas Prominent Leaders- Events leading to the formation of Andhra State 1953. Role of Press and News Papers in the Andhra Movement. Role of Library Movement and Folk and Tribal Culture.
5.Events leading to the Formation of Andhra Pradesh State – Visalandhra Mahasabha – States Reorganization Commission and its Recommendations Gentlemen Agreement – Important Social and Cultural Events between 1956 and 2014.
INDIAN CONSTITUTION
6.Nature of the Indian Constitution Constitutional Development – Salient features of Indian Constitution – Preamble – Fundamental Rights, Directive Principles of State Policy and their relationship – Fundamental Duties, Distinctive features – Unitary and Federal.
7.Structure and functions of Indian Government – Legislative, Executive and Judiciary Types of Legislatures – Unicameral, Bicameral- Executive – Parliamentary, Judiciary- Judicial Review, Judicial Activism.
8.Distribution of Legislative and Executive Powers between the Union and the States; Legislative, Administrative and Financial relations between the Union and the States – Powers and the Functions of Constitutional Bodies UPSC, State Public Service Commissions, CAG and Finance Commission.
9.Centre State relations- Need for Reforms- Rajmannar Committee, Sarkaria Commission, M.M. Punchchi Commission – Unitary and Federal features of Indian Constitution.
10.Amendment Process to the Constitution Centralization Vs Decentralization – Community Development Programs- Balwantray Mehta, Ashok Mehta Committees 73rd and 74th Constitutional Amendment Acts and their Implementation.
11.Indian Politacal Parties- National, Regional- One Party, Bi-Party, Multi-Party Systems- Regionalism and Sub-Regionalism-Demand for New States – Sri Krishna Committee – National Integration Threats to Indian Unity.
12.Welfare Mechanisms in India-Provisions for Scheduled Castes, Tribes and Minorities, Reservations for SCs, STs and Backward Classes Prevention of SCs and STs Atrocities Act- National and State SCs, STs and BCs Commissions, Women's Commission, National and State Minorities Commissions – Human Rights Commission – RTI – Lokpal and Lok Ayukt.
Section – C
PLANNING AND ECONOMY
1.Indian Economy and Present Status:
Socio-Economic- Goals and Achievements – New economic reforms 1991. Regulation of the Economy – Creation of regulatory bodies NITI Aayog- Co-operative Federalism and decentralization of financial resources – Lack of inclusive growth and sustainable development: causes, consequences and solutions.
2.Indian Economic Policies:
Agricultural policies – Contribution of agriculture to India's GDP – Issues of financing, Production, marketing and distribution of agriculture.
Industrial policies- Main features of industrial development in India – Sectoral composition – Roles of private and public sectors in employment, productivity – Role of IT industries in development.
3.Resources and Development:
Types of resources – Physical capital and finance capital – Population size, composition and growth-Trends; Occupational Distribution of Work force – Human Development Indexas a measurement of development. Demographic Dividend.
4.Money, Banking and Public Finance:
Monetary policy of RBI – Fiscal policy – Objectives – Fiscal Imbalance and Deficit Finance – New Foreign Trade Policy. Current account imbalances; FDI.
Inflation, its causes and remedies; Budget – taxes and non-tax revenue. Goods and Service Tax (GST)
5.National Income:
National Income and concepts – Gross Domestic Product – Net Domestic Product, Per capita income.
6.Economic Policies of Andhra Pradesh:
Socio Economic welfare Programmes of Government of Andhra Pradesh. Composition of Population in Andhra Pradesh – Rural – Urban, Sex Ratio, Age Distribution.
7.Agriculture and Industrial Growth of Andhra Pradesh:
Contribution of agriculture to income and employment in Andhra Pradesh. Land reforms in Andhra Pradesh – Cropping pattern – Irrigation Policy of Andhra Pradesh – sources of agricultural finances agricultural subsidies – public distribution system in Andhra Pradesh.
Industrial Development in Andhra Pradesh – Growth and structure of industries – Incentives to industries – Industrial corridors in and SEZs in Andhra Pradesh – Bottlenecks for industrial development power projects.
8.Resource Development of Andhra Pradesh:
Andhra Pradesh Budgetary resources and constraints – Fulfillment of the conditions of A.P Bifurcation Act – central assistance and issues of conflict – public debt and projects of external assistance. Andhra Pradesh State Gross Domestic Product – Comparison with India and neighboring States.
GROUP-II
MAINS EXAMINATIONS
Paper – I
General Studies and Mental Ability
1.Events of national and international importance.
2.Current affairs international, national and regional.
3.General Science and its applications to the day to day life Contemporary developments in Science and Technology and Information Technology.
4.Social economic and political history of modern India with emphases on Indian national movement.
5.Indian polity and governance: constitutional issues, public policy, reforms and e-governance initiatives.
6.Geography of India with focus on Andhra Pradesh.
7.Disaster management: vulnerability profile, prevention and mitigation strategies, Application of Remote Sensing and GIS in the assessment of Disaster.
8.Sustainable Development and Environmental Protection.
9.Logical reasoning, analytical ability and logical interpretation.
10.Data Analysis: Tabulation of data Visual representation of data Basic data analysis (Summary Statistics such as mean, median, mode and variance) and Interpretation.
11.Bifurcation of Andhra Pradesh and its Administrative, Economic, Social, Cultural, Political and legal implications/problems.
Paper – II
Social and Cultural History of Andhra Pradesh
1.Social and Cultural History of Andhra Pradesh: Geographical Features of Andhra – Its Impact on History and Culture – Pre-historic Cultures – The Satavahanas, The Ikshvakus – Socio-economic and Religious Conditions – Literature, Art and Architecture – The Vishnukundins, The Eastern Chalukyas of Vengi, Telugu Cholas-Society, Religion, Telugu Language, Literature, Art and Architecture.
2.Various Major and Minor dynastices that ruled Andhradesa between 11th and 16th centuries A.D. Socio Cultural and Religious conditions in Andhradesa between 11th to 16th centuries A.D, Social structure, Caste System, Status of Women. Growth of Telugu Language, Literature, Art, Architecture and Painting.
3.Advent of Europeans- Trade centers – Andhra under the Company 1857 Revolt and its impact on Andhra Establishment of British Rule Sociocultural awakening, Justice Party/Self Respect Movements Growth of Nationalist Movement in Andhra between 1885 to 1947 Role of Socialists – Communists – Anti Zamindari and Kisan Movements. Growth of Nationalist Poetry, Revolutionary Literature, Nataka Samasthalu and Women Participation.
4.Origin and growth of Andhra Movement Role of Andhra Mahasabhas Prominent Leaders- Events leading to the formation of Andhra State 1953. Role of Press and News Papers in the Andhra Movement. Role of Library Movement and Folk and Tribal Culture.
5.Events leading to the Formation of Andhra Pradesh State – Visalandhra Mahasabha – States Reorganization Commission and its Recommendations Gentlemen Agreement – Important Social and Cultural Events between 1956 and 2014.
INDIAN CONSTITUTION
6.Nature of the Indian Constitution Constitutional Development – Salient features of Indian Constitution – Preamble – Fundamental Rights, Directive Principles of State Policy and their relationship – Fundamental Duties, Distinctive features – Unitary and Federal.
7.Structure and functions of Indian Government – Legislative, Executive and Judiciary Types of Legislatures – Unicameral, Bicameral- Executive – Parliamentary, Judiciary- Judicial Review, Judicial Activism.
8.Distribution of Legislative and Executive Powers between the Union and the States; Legislative, Administrative and Financial relations between the Union and the States – Powers and the Functions of Constitutional Bodies UPSC, State Public Service Commissions, CAG and Finance Commission.
9.Centre State relations- Need for Reforms- Rajmannar Committee, Sarkaria Commission, M.M. Punchchi Commission – Unitary and Federal features of Indian Constitution.
10.Amendment Process to the Constitution Centralization Vs Decentralization – Community Development Programs- Balwantray Mehta, Ashok Mehta Committees 73rd and 74th Constitutional Amendment Acts and their Implementation.
11.Indian Politacal Parties- National, Regional- One Party, Bi-Party, Multi-Party Systems- Regionalism and Sub-Regionalism-Demand for New States – Sri Krishna Committee – National Integration Threats to Indian Unity.
12.Welfare Mechanisms in India-Provisions for Scheduled Castes, Tribes and Minorities, Reservations for SCs, STs and Backward Classes Prevention of SCs and STs Atrocities Act- National and State SCs, STs and BCs Commissions, Women's Commission, National and State Minorities Commissions – Human Rights Commission – RTI – Lokpal and Lok Ayukt.
Paper-III
PLANNING AND ECONOMY
1.Indian Economy and Present Status:
Socio-Economic- Goals and Achievements – New economic reforms 1991. Regulation of the Economy – Creation of regulatory bodies NITI Aayog- Co-operative Federalism and decentralization of financial resources – Lack of inclusive growth and sustainable development: causes, consequences and solutions.
2.Indian Economic Policies:
Agricultural policies – Contribution of agriculture to India's GDP – Issues of financing, Production, marketing and distribution of agriculture.
Industrial policies- Main features of industrial development in India – Sectoral composition – Roles of private and public sectors in employment, productivity – Role of IT industries in development.
3.Resources and Development:
Types of resources – Physical capital and finance capital – Population size, composition and growth-Trends; Occupational Distribution of Work force – Human Development Indexas a measurement of development. Demographic Dividend.
4.Money, Banking and Public Finance:
Monetary policy of RBI – Fiscal policy – Objectives – Fiscal Imbalance and Deficit Finance – New Foreign Trade Policy. Current account imbalances; FDI.
Inflation, its causes and remedies; Budget – taxes and non-tax revenue. Goods and Service Tax (GST)
5.National Income:
National Income and concepts – Gross Domestic Product – Net Domestic Product, Per capita income.
6.Economic Policies of Andhra Pradesh:
Socio Economic welfare Programmes of Government of Andhra Pradesh. Composition of Population in Andhra Pradesh – Rural – Urban, Sex Ratio, Age Distribution.
7.Agriculture and Industrial Growth of Andhra Pradesh:
Contribution of agriculture to income and employment in Andhra Pradesh. Land reforms in Andhra Pradesh – Cropping pattern – Irrigation Policy of Andhra Pradesh – sources of agricultural finances agricultural subsidies – public distribution system in Andhra Pradesh.
Industrial Development in Andhra Pradesh – Growth and structure of industries – Incentives to industries – Industrial corridors in and SEZs in Andhra Pradesh – Bottlenecks for industrial development power projects
8.Resource Development of Andhra Pradesh:
Andhra Pradesh Budgetary resources and constraints – Fulfillment of the conditions of A.P Bifurcation Act – central assistance and issues of conflict – public debt and projects of external assistance. Andhra Pradesh State Gross Domestic Product – Comparison with India and neighboring States.
SCHEME
Screening Test (Objective Type)
(Degree Standard)
|
Written Examination (Objective Type) |
No. of Questions |
Duration (Minutes) |
Maximum Marks |
|
Part-A General Studies & Mental Ability |
75 |
75 |
150 |
|
Part-B Rural Development and Problems in Rural Areas with special reference to Andhra Pradesh |
75 |
75 |
|
|
Negative Marks: As per G.O.Ms. No. 235, Finance (HR-I, Plg & Policy) Dept; Dt 06/12/2016, for each wrong answer will be penalized with 1/3rd of the marks prescribed for the question. |
|||
1.Events of national and international importance
2.Current affairs – international, national and regional
3.General Science and it applications to the day to day life Contemporary developments in Science & Technology and information Technology
4.Social- economic and political history of modern India with emphasis on Andhra Pradesh.
5.Indian polity and governance: constitutional issues, public policy, reforms and e-governance initiatives with specific reference to Andhra Pradesh.
6.Economic development in India since independence with emphasis on Andhra Pradesh.
7.Physical geography of Indian sub-continent and Andhra Pradesh.
8.Disaster management: vulnerability profile, prevention and mitigation strategies, Application of Remote sensing and GIS in the assessment of Disaster.
9.Sustainable Development and Environmental Protection
10.Logical reasoning, analytical ability and data interpretation.
11.Data Analysis:
(a)Tabulation of data
(b)Visual representation of data
(c)Basic data analysis (Summary statistics such as mean median, mode, variance and coefficient of variation) and Interpretation
12.Bifurcation of Andhra Pradesh and its Administrative, Economic, Social, Cultural, Political and Legal implications./problems.
Main Examination
(Degree Standard)
Written Examination (Objective Type) | No. of Questions | Duration (Minutes) | Maximum Marks |
Part-A General Studies & Mental Ability | 150 | 150 | 150 |
Part-B Rural Development and Problems in Rural Areas with special reference to Andhra Pradesh | 150 | 150 | 150 |
Total | 300 | ||
Negative Marks: As per G.O.Ms. No. 235, Finance (HR-I, Plg & Policy) Dept; Dt 06/12/2016, for each wrong answer will be penalized with 1/3rd of the marks prescribed for the question | |||
1.Evolution of Panchayat Raj system in India including Constitutional amendments and reports of various Committees.
2.Evolution of Panchayat Raj system in Andhra Pradesh.
3.Roles and responsibilities of Panchayat Secretary.
4.Rural Sociology: History and Evolution of schemes catering to upliftment of Rural Poor.
5.Flagship Rural Development schemes of Rural Development Department of Government of India and Andhra Pradesh.
6.Key Schemes of Panchayat Raj Department of Andhra Pradesh.
7.Rural Economy of Andhra Pradesh: Agriculture, Small scale Industries, Rural artisans.
8.Rural Credit Scenario of Andhra Pradesh: Role of Banks, co-operatives and Micro Finance.
9.Community Based Organizations and convergence of Welfare Schemes.
10.Women Empowerment and Economic development through Self Help Groups
11.Revenue and Expenditure Management of Local Bodies
12.Accounting and administering funds received under various schemes.
GROUP- 4. SYLLABUS
SSC LEVEL
General studies paper -1
1. History, Economics, Civics and Geography.
2.Physical Science
3.Natural Science
4.Current Affairs
5.Reasoning and Analytical Ability.
6.Basic things about disaster management (CBSE – VIII & IX Standard)
7.Bifurcation of Andhra Pradesh.
8.Sustainable Development and Environmental Protection.
9.Bifurcation of Andhra Pradesh and its Administrative, Economic, Social, Cultural, Political and legal implications/problems, Including.
(a) Loss of capital city, challenges in building new capital and it's financial implications.
(b) Division and rebuilding of common Institutions.
(c) Division of employees, their relocation and nativity issues.
(d) Effect of bifurcation on commerce and entrepreneurs.
(e) Implications to financial resources of state government.
(f) Task of post-bifurcation infrastructure development and opportunities for investments.
(g) socioeconomic, cultural and demographic impact of bifurcation.
(h) Impact of bifurcation on river water sharing and consequential issues
(i) AP REORGANISATION ACT, 2014 on AP and the arbitrari ness of certain provisions
ECONOMICS
1.Economic Growth and Development – Indicators of Economic Development – Characteristic Features of Developing Countries like India.
2.National Income – Concepts of National Income – GNP – NNP – Percapita Income – Disposable Income – Estimation of National Income – Trends in National Income – Structural Changes in Indian Economy – Sectoral Distribution of GDP.
3.Planning and Economic Reforms in India – Meaning of Planning – Objectives – India's Five Year plans – NITI AYOG – Twelth Five Year Plan – Eradication of Poverty and Reduction of Unemployment Programmes.
4.Environment and Sustainable Development – Concepts of Environment – Linkages Between Environment and Economy – Environmental Pollutions Types – Measures to Control Pollution – Sustainable Economic Development.
5.Economy of Andhra Pradesh – Economic History of Andhra Pradesh – Characteristic features – Demographic features – Occupational Distribution of workforce – Development of Agricultural Sector, Industry and Service Sectors – Welfare measures.
2. Natural Sciences
Introduction to living organisms, Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells. Structure, reproduction and uses of bacteria. Nature of viruses. Common diseases caused by bacteria and viruses. Plant kingdom, and Animal kingdom – salient features of Algae, Fungi, Bryophytes, Pteridophytes, Gymnosperms, invertebrates and vertebrates. Uses of plants in food, fibre and medicine. Crop plants, Uses of animals in food and medicine.
3.Physical Sciences
Matter, Mechanics, Sound, Heat, Optics, Electricity, Electro Magnetism and their applications in the day to day life. Chemical equation and reaction, Acids, Basis and Salts, Structure of Atom, Classification of Elements, Chemical bonding, Carbon it Compounds, Metallurgy.
4. History
History of Modern India with a focus on Indian National Movement. Important Cultural Events in Andhra Pradesh up to 1956 – Economic Challenges Faced by Andhra Pradesh post Bifurcation in 2014.
Paper-2
Secretarial Abilities
1.Mental Ability (Verbal and Nonverbal)
2.Logical Reasoning
3.Comprehension
(a)Descriptive Passage
(b)Logical Passage
(c)Narrative Passage
4.(a) Re-arrangement of sentences with a view to improving the structure of a passage.
(b) Spelling, Punctuation, Proof-Reading, Editing Skills
5.Numerical and Arithmetical abilities.
Syllabus for Preliminary Written Examination
(Degree Standard)
Paper-I
Arithmetic: It will include questions on problems relating to number system, simple interest compound interest ratio & proportioryaverage, percentage, profit & loss, time & work, work & wages, time & distance, clocks & calendars, partnership, mensuration etc.
Test of Reasoning: It will include questions of both verbal & non-verbal type and include question on analogies, similarities and differences, spatial visualisatiory spatial orientatiory problem solving, analysis, judgment decision making, visual memory etc.
Paper II: General Studies (Degree Standard) (100 Questions)
1.General Science: contemporary developments in science and technology and their implications including matters of everyday observation and experience, contemporary issues relating to protection of environment as may be expected of a well educated person who has not made a special study of any scientific discipline.
2.Current events of national and international importance.
3.History of India – emphasis will be on broad general understanding of the subject in its social, economic, cultural and political aspects. Indian National Movement.
4.Geography of India
5.Indian Polity and Economy – including the Country's political system rural development, planning and economic reforms in India.
Syllabus for final written examination (degree standard)
Short essay, comprehension, precis, letter writing paragraph writing/report writing
Paper I: English (Degree Standard)
The candidate's understanding of the English language, its correct usage and his writing ability would be tested. Questions on short essay, comprehensiory procis, letter writing, paragraph writing/report writing, kanslation from English to Telugu etc. would be included.
The candidate's understanding of the Telugu language, its correct usage and his writing ability would be tested. Questions on short essay, comprehension, procis, letter writing paragraph writing/report writing, translation from Telugu to English etc. would be included.
Arithmetic (SSC Standard) & Test of Reasoning Mental Ability (200 Questions)
Arithmetic: It will include questions on problems relating to number system, simple interest, compound interest, ratio & proportion, average, percentage, profit & loss, time & work, work & wages, time & distance, clocks & calendars, partnership, mensuration etc.
Test of Rcasonine: It will include questions of both verbal & nonverbal type and include question on analogies, similarities and differences, spatial visualisation, spatial orientatiory problem solving, analysis, judgment, decision making, visual memory etc.
General Studies (Degree Standard) (200 Questions)
1.General Science – contemporary developments in science and technology and their implications including matters of everyday observation and experience, contemporary issues relating to protection of environment as may be expected of a well educated person who has not made a special study of any scientific discipline.
2.Current events of national and international importance
3.History of India – emphasis will be on broad general understanding of the subject in its social, economic, cultural and political aspects. Indian National Movement.
4.Geography of India
5.Indian Polity and Economy – including the Country's political system, rural development planning and economic reforms in India.
CONSTABLE SYLLABUS:
1.English
2.Arithmetic
3.General Science
4.History of India, Indian culture, Indian National Movement
5.Indian Geography, Polity and Economy
6.Current Events of national and international importance
7.Test of Reasoning/Mental Ability
Award of marks: For each question the candidate will be awarded full marks, if he darkened only one bubble corresponds to the correct answer. Incase, the candidate has not darkened any bubble, he will be awarded zero mark for that question.
JL, DL General Studies Syllabus
Part-A: Written Examination (Objective Type) | |||
Papers | No. of Questions | Duration (Minutes) | Maximum Marks |
Paper 1 : General Studies & Mental Ability | 150 | 150 | 150 |
Paper 1 : Concerned Subject (One only) | 150 | 150 | 300 |
Part B : Interview (Oral Test) | 50 | ||
Total | 500 | ||
Negative Marks: As per G.O.Ms. No. 235, Finance (HR-I, Plg & Policy) Dept; Dt 06/12/2016, for each wrong answer will be penalized with 1/3rd of the marks prescribed for the question | |||
1.Events of national and international importance
2.Current affairs – international, national and regional
3.General Science and it applications to the day to day life contemporary developments in Science & Technology and information Technology
4.Social – economic and political history of modern India with emphasis on Andhra Pradesh.
5.Indian polity and governance: constitutional issues public policy, reforms and e-governance initiatives with specific reference to Andhra Pradesh.
6.Economic development in India since independence with emphasis on Andhra Pradesh.
7.Physical geography of Indian sub-continent and Andhra Pradesh.
8.Disaster management: vulnerability profile, prevention and mitigation strategies, Application of Remote Sensing and GIS in the assessment of Disaster.
9.Sustainable Development and Environmental Protection
10.Logical reasoning, analytical ability and data interpretation.
11.Data Analysis:
(a)Tabulation of data
(b)Visual representation of data
(c)Basic data analysis (summary statistics such as mean, median, mode, variance and coefficient of variation) and Interpretation
12.Bifurcation of Andhra Pradesh and its Administrative, Economic, Social, Cultural, Political and Legal implication/problems.
(GROUP-I SERVICES)
(HONS. DEGREE STANDARD)
|
(SUBJECT) |
DURATION (HOURS) |
MAXIMUM MARKS |
|
Preliminary Test General Studies & Mental ability (objective Type) 150 Questions
Paper– I General Essay) It will have to cover the following topics
|
2 ½ 3 3 |
150 150 150 |
|
Paper-II: History, Culture and Geography
|
3 |
150 |
|
Paper-III: Indian Society, Constitution and Governance
|
3 |
150 |
|
Paper-IV: Economy and Development
|
3 |
150 |
|
Paper-V: Science & Technology and Data Interpretation)
|
3 |
150 |
|
Paper-VI: Telangana Movement and State Formation
|
3 |
150 |
|
(Total Marks) (Interview) (Grand Total) |
900 100 1000 |
|
GROUP-I SERVICES (PRELIMINARY TEST) |
- Current Affairs- Regional, National & International.
- International Relations and Events.
- General Science; India's Achievements in Science and Technology.
- Environmental Issues: Disaster Management- Prevention and Mitigation Strategies.
- Economic and Social Development of India.
- World Geography, Indian Geography and Geography of Telangana state.
- History and Cultural Heritage. of India.
- Indian Constitution and Polity.
- Governance and public policy in India.
- Policies of Telangana. State.
- Society, Culture, Heritage, Arts and Literature of Telangana.
- Social Exclusion: Rights issues such as Gender, Caste, Tribe, Disability etc. and inclusive policies.
- Logical Reasoning: Analytical Ability and Data Interpretation.
MANINS WRITTEN TEST
GENERAL ENGLISH ( QUALIFYING EXAM)
( Eligibilityfor 10th class levelinterview)
- Spotting Errors-Spelling: Punctuation
- Fill in the blanks- Preposition: Conjuctions; Verb tenses
- Re-writing sentences- Active and Passive voice; Direct & Reported Speech; Usage of vocabulary
- Jumbled sentences
- Comprehension
- Percis Writing
- Expansion
- Letter Writing
PAPER-I: GENERAL ESSAY
(Candidate should write three Essays, selecting one from each Section compulsorily. Each Section contains three Questions. Each Essay carries 50 marks.)
1:
- Contemporary Social Issues and Social Problems.
- Issues of Economic Growth and Justice.
2:
- Dynamics of Indian Politics.
- Historical and Cultural Heritage of India.
3:
- Developments in Science and Technology.
- Education and Human Resource Development.
PAPER-II: HISTORY, CULTURE AND GEOGRAPHY
I.History and Culture of India, with special reference to Modern Period (1757 to 1947 A.D.)
- Early Indian Civilization-Indus and Vedic; Emergence of Religious Movements in the sixth century BC – Jainism and Buddhism; Indo- Greek Art and Architecture – Gandhara, Mathura and Amaravathi Schools; Social and Cultural condition under the Mauryan, Satavahanas and Guptas.
- Advent of Islam and its impact on Indian Society – Nature and significance of Bhakti and Sufi Movements; Contribution of Kakatiya, and Vijayanagara rulers to Language, Literature, Art and Architecture: the contribution of Delhi Sultans and Mughals to Language, Literature, Art Architecture and Fine Arts, Monuments; Emergence of Composite Culture in the Deccan and India.
- The Establishment of British Colonial Rule in India: Carnatic Wars, Battle of Plassey, Anglo- Mysore, Anglo-Maratha and Anglo-Sikh Wars; Economic Impact of British Colonial Rule: Land Revenue Settlements in British India; -Commercialization of Agriculture; Rise of Landless Agrarian Labour; Famines and Poverty; De-industrialization; Decline of Traditional Crafts; Drain of Wealth; Growth of Trade and Commerce- Economic Transformation of India; Railroads, Transport and Communication Network- Telegraph and Postal Services.l
- Anti- British uprisings: Tribal and peasant revolts in the Nineteenth Century-Causes and Consequences of 1857 revolt. Factors responsible for the rise of Indian Nationalism; Rise and Growth of Socio- Religious and Anti-Caste Movements: Brahma Samaj, Arya Samaj, Aligarh Movement, Satya Shodak Samaj, Jotiba and Savithribhai Phule, Pandita Ramabai, Narayana Guru, Ayyankali, Annie Beasant; Non- Brahmin, Justice and Self-Respect Movements: Periyar Mahatma Gandhi Ambedkar and others.
- Three Phases of Indian Freedom Struggle, 1885-1947. The rise and growth of all India Kisan Sabha, Workers and Tribal movements; Issue of Gender and Women's movement; Growth of Socialist and Communist Movements; Growth of Communalism; Independence and Partition of India.
II.History and Cultural Heritage of Telangana.
\- History and culture of Ancient Telangana - Satavahanas, Ikshvakus and Vishnukundins; Rise and growth of Jainism and Buddhism; Socio-Cultural – Conditions – Language, Literature, Art and Architecture.
- Medeival Telangana and the emergence of composite culture-Kakatiyas and Velama kingdoms and their contribution to Socio-Cultural Development, Literature, Music, Dance, Art and Architecture; Qutub Shahis and their contribution to Telugu literature, art and architecture. Protest Movements against Kakatiyas and Qutub Shahis- Sammakka Sarakka and Saraipapanna.
- The Establishment of Asaf Jahi Dynasty – Salar Jung Reforms and Modernization of Telangana; socio-Economic development under the Nizams – Land Tenures and Social System, Jagirdars, Deshmukhs etc. and Vetti-British Paramountcy and Nizam-Revolt of 1857 in Hyderabad and the role of Turre Baz Khan; Socio-Economic Development during the rule of the sixth and seventh Nizams – Growth of Railways, Transport and Communication System, Establishment of Industries, Educational Institutions – Monuments of Asaf Jahi period.
- Socio- cultural awaking in telangana – Andhra sarasvath parishat literary and library movement ; establishment of nizam rashtra Andhra jana sangham - -andhra mahasabha – social reformmovements –brahama samaj, Arya samaj andadi-hinduand dalitmovements, roal ofbhagyareddyvarma – Andhra mahila sabha and the growthof women’smovement . Role of Hyderabad state cogress and vandemataram movement.
- People Movement against the Nizam's Rule – Adivasi Revolts – Ramji Gond and Kumaram Bheemu- Telangana Peasants Armed Struggle – Role of Andhra Mahasabha and the Communists – Majlis-Ittehadul- Muslimeen Party, Rajakars and Kasim Razvi – Police Action and the End of Nizam's Rule – Integration of Hyderabad State into Indian Union.
III.Geography of India and Telangana.
- India - Physical setting, Physiography, Drainage, Climate- Mechanism of Monsoon, effect of EI- Nino and La Nino, Rainfall variability- Floods and drought, Soils, Vegetation and Wildlife-Degradation and Conservation Measures. Major Minerals and Energy Resources-distribution and conservation, Energy Crisis-role of non-conventional energy resources. Marine Resources-Economic significance, EEZ. Water resources-availability, problems of inter-state Water sharing, Conservation Measures.
- Agriculture and Irrigation-Major Food and Non-Food crops, Agro Climatic Regions, Green Revolution, recent trends in Agriculture; Major Irrigation Projects and Command Area Development; Industries-Major Industries-Iron and Steel, Cotton Textiles, Cement, Sugar, Automobile, IT, & Food Processing Industries, Localisation Factors, Industrial Corridors & Economic Development; Transportation: Means of Transportation, Role of Road and Rail Network in Economic Development, Highways and Express Highways; Major Ports – changing trends and direction of India's Trade – role of WTO; Strategic location of India in the Indian Ocean; Population – distribution, growth, demographic characteristics, demographic dividend and transition, HDI, Population problems and Policies, Urbanisation process- Spatial pattern, growth of Megacities, problem of Urban Growth and Policies, concept of Smart Cities.
- Geographical extent of Hyderabad State and present Telangana State Physical setting, Relief, Climate, Rivers, Soils, Forest cover and Wild life-distribution, depletion and conservation. Minerals and Energy resources – Coal, Iron and Limestone distribution. Thermal and Hydro Power projects – Problems and Prospects.
- Agriculture- Rainfed/Dry land Agriculture, Drought prone areas and Mitigation Measures. Sources of Irrigation: Canals, Tanks and Wells, Depletion of Ground Water and its conservation- Mission Kakatiya. Industries – Cement, Sugar, Pharma, Electronic, Tourism, IT, ITIR, SEZs. Handicrafts and Household Industries and their problems. Road and Rail Network distribution and role in Economic Development. Population – distribution, growth, density, demographic characteristics (sex ratio, age, literacy, etc.,) Tribal Population – distribution, problems of Tribal areas and Policies for Tribal Area Development.
- Urbanisation in Telangana State. Spatio-temporal changes, Urban Growth and Migration. Evolution and phases of Urban Growth of Hyderabad, transformation from historical to modern cosmopolitan Megapolis, Primacy of Hyderabad in Telangana State, City structure, Industries and Industrial estates, urban infrastructure and transport – ORR and Metro – Problems and planning- role of GHMC and HUDA (Metropolitan Development Plan – 2031, HMDA), Hyderabad as a Tourist Centre and Global city.
PAPER-III: INDIAN SOCIETY, CONSTITUTION AND GOVERNANCE
I.Indian Society, Structure, Issues and Social Movement:
- Indian Society: Salient features, Unity in Diversity; Family, Marriage, Kinship, Caste, Tribe, Religion, Language; Rural – Urban continuum; Multi-culturalism.
- Social Exclusion and Vulnerable Group: Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes, Backward Classes, Minorities, Women, Children, Aged and Disabled.
- Social Issues: Poverty; Unemployment, Child Labour, Violence against Women; Regionalism; Communalism and Secularism; Corruption; Caste Conflicts, Problems of Agricultural Labour; Urbanization; Development and Displacement; Environmental Degradation; Sustainable development; Population Explosion; Agrarian Distress; Migration.
- (a) Social Issues in Telangana; Vetti; Jogini and Devadasi System; Girl Child; Flourosis; Child Labour; Migrant Labour; Child Marriages.
(b) Social Movements in Telangana. - Social Policies and Programmes in India and Telangana: Policies for Women, Children, Aged and Disabled; policies for Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes, Backward Classes and Minorities; Environmental Policy; Population Policy; Policy on education; Policy on Health; Poverty Alleviation Programmes; Welfare Schemes for Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes, Backward Classes, Women, Children, Minorities, Aged and Disabled.
II.Constitution of India.
- Evolution of Indian Constitution: Role of the Drafting Committee; Constitutional Philosophy and Preamble; Salient & Basic Structure; Amendments.
- Fundamental Rights; Nature and Scope; Expanding horizons of Fundamental Rights; Enforceability against State and others; Welfare State and Distributive Justice under the Constitution; Directive Principles of State Policy – Rule of Law and Fundamental Duties.
- System of Government: Parliamentary system, Central Government: President, Prime Minister & Council of Ministers; Parliament: Powers and Function; State Government: Governor, Chief Minister & Council of Ministers; Legislature: Powers and Functions, Legislative Privileges.
- Judicial System in India: Supreme Court, High Courts & Administrative Tribunals; Subordinate Judiciary; Judicial Review and Judicial Activism; Independence of Judiciary and Judicial Accountability.
- Federal system: Centre-State Relations- Issues and Challenges pertaining to the Federal Structure; Local Self-Government 73rd and 74th Constitutional Amendments for sharing of powers – Panchayat Raj and Municipal Institutions; Resolution of Inter-State disputes with reference to Water Disputes- Challenges of Implementation.
III.Governance:
- Governance and Good Governance, E-Governance-Applications and Models; Governance at Union level-Cabinet Secretariat, Prime Minister's office (PMO), Central Secretariat, Ministries and Departments; Constitutional bodies-Finance Commission, Election Commission, Union Public Service Commission, Comptroller and Auditor General of India, National Human Rights Commission, National Commission for SCs/ST/Minorities and Women; Parliamentary Committees-Estimates Committee, Public Accounts Committee, Committee on Public Undertakings.
- Governance at State and District level-Secretariat and Directorates and their relationship; District Administration-Role of Collector, Institutions of Rural and Urban Governance-Powers and Functions, Systems for delivery of Services; Cooperatives, State Finance Commission; Devolution of Powers and Finances-Issues and Challenges. Development Corporations for SCs, STs, BCs, minorities and Disabled Welfare; Control over Administration- Legislative, Executive and Judicial Control.
- Programmes, Agencies and Institutions working for the development of Urban and Rural Areas; People Centred Participatory Development; Poverty Alleviation Programmes; Women Empowerment and Inclusive Growth; Rights related to Health, Food Security and Education-Issues and Challenges.
- Debates on Development and Development Processes; State and Provision of Services; State and Market; Involvement of Civil Society-Community Based Organizations (SHGs), Charities and Stakeholders, Public-Private Partnerships (PPP); Corporate Social Responsibility.
- Ethics and Values of Administration; Neutrality of Civil Services, Committed Bureaucracy, Politician and Civil Servant Relations; Citizen Charters, Gender Sensitization; Transparency and Accountability of Administration; Prevention of Corruption in Administration- Central Vigilance Commission, Central Bureau of Investigation, Lokpal, Lokayuktha, ACB and Consumer Protection Mechanisms; Application and Impact of Right to Information Act-2005; Administrative Reforms.
ECONOMY AND DEVELOPMENT
I.Indian Economy and Development.
- National Income-Concepts and Measurement of National Income-Nominal and Real Income; Structure and growth of Indian economy- Sectoral trends in National Income of India.
- Poverty capability approach (Human Poverty Index), Poverty and Unemployment: Concepts of Poverty – Income-based Poverty, Non-Income Poverty-capability approach (Human Poverty Index), Measurement of Poverty and trends in Poverty; Concepts, estimates and trends of Unemployment
- Money and Banking: Money supply, Structure of Indian Banking and non-banking financial institutions; Reforms in Banking sector; Regulation of credit by RBI.
- Public Finance: Tax Structure, Central and state taxes; Government expenditure in revenue and capital account; Public debt: composition- internal and external debt; Monetary Policy, Fiscal Policy; Union Budget: Budget Analysis.
- Planning in Indian economy: objectives, Priorities, Strategies, Achievements of Five Year Plans; 12th FYP – Inclusive growth; NITI Aayog; Liberalization, Privatisation, Globalisation: Features and Implications.
II.Telangana Economy:
- Telangana economy in Hyderabad State (Agriculture, Industry and Trade); Telangana economy in United AP (1956-2014)-Deprivation and Under development; Structure and Growth of Telangana economy: Sectoral trends in GSDP; per capita income; Income inequalities and Poverty.
- Human resources: Demographic Structure and Transition Demographic dividend, (sex ratio, fertility rate, mortality rates); Literacy and Occupation structure.
- Land reforms: I generation (1947-1970) and II generation land reforms (1970- onwards)- Abolition of Intermediaries : Zamindari, Jagirdari and Inamdari –Tenancy Reforms : Land ceiling ; Land alienation in Scheduled areas ; Impact of land reforms.
- Agriculture and Allied sectors: Trends in share of crop and allied sectors in GSDP; Distribution of land holdings; Trends in Irrigation; Problems of dry land Agriculture; Dependence on Agriculture; Cropping pattern Trends ; Trends in productivity; Agricultural Credit, Extension and Marketing; Cooperatives and producer Companies.
- Industry and Service sectors: Industrial development; Structure and growth of Industrial sector, Micro Small and Medium Enterprises (MSME) sector, Revival of sick industries; Industrial infrastructure- Power; Industrial Policy of Telangana; Structure and growth of service sector; employment trends in Industry and Service sectors; Information and Communication Technology (ICT) policy of Telangana.
III.Development and Environmental Problems.:
- Environment vs Development: Definition of Environment, Environmentalism; Environmental Protection Policy, Environmental Policy Instruments.
- Natural resources: Forest resources- Commercialization of forests – Forest Acts vs Forest dwellers/users; Water: Surface water and groundwater, competing demand for water – drinking, Industrial and agriculture; Land resources: competing uses of land-food, feed, fuel, and fibre; Mining and Environment; Sustainability of natural resources.
- Eco systems and Bio-diversity: Ecology and Eco-system; Food chains in Eco system, Typology of eco system; Bio diversity and its conservation, Types of Bio diversity, threat to Bio diversity.
- Environment pollution and solid waste management, types of solid waste, factors affecting solid waste generation, impact of solid waste, recycling and reuse.
- Global Environment Issues: Climate Change, Global Warming and its impact, Sustainable Development.
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY AND DATA INTERPRETATION :
I.The role and impact of Science and Technology.
- Classical and Emerging areas of Science & Technology : Value addition by Science & Technology, Current Science & Technology developments in India and importance of Science & Technology as an engine for National Development ; Industrial development & Urbanization.
- National Policy of Science & Technology: changes in Policy from time to time: Technology mission – ICT: Basics in Computers, Robotics, Nano technology and Communication.
- Space program in India and its applications with special reference to industrial, agricultural and other rural development activities, INSAT, IRS systems, EDUSAT and Chandrayaan-1 and future programme.
- Application of Space Technology in India with references to Education, Agriculture and Industry. Climatic change, Floods, Cyclone, Tsunami, Natural and Manmade Disaster Management.
- Energy Resources: Energy demands, Indian energy scenario- hydel, thermal and nuclear. Importance of renewable resources – Solar, Wind, small/Mini/Micro hydel, Biomass, waste based, geothermal, tidal & fuel cells. Energy security – Role of Science & Technology, Bio-fuel cultivation and extraction.
II.Modern Trends in application of knowledge of Science.
- Crop Science in India; Characteristics of Plants-Crop plants, Forest species, Medicinal Aromatic plants, Useful and Harmful plants and utility for mankind.
- Concept of Biotechnology and application of genetic engineering and Stem Cell Research. Biotechnology in Agriculture (bio-fertilizers, bio – pesticides, bio- fuels, tissue culture, cloning) and Environment (Biotechnology in Environmental cleanup process).
- Food bio-technology, Food safety and Food quality standards, Food Laws and Regulations. Recent trends in organic farming and farm mechanization Safe Drinking Water – Defluoridation and other Techniques.
- Microbial infections; Introduction to bacterial, viral, protozoal and fungal infections. Basic knowledge of infections caused by different groups of micro organisms- diarrhea, dysentera, cholera, tuberculosis, malaria, viral infections like HIV, encephalitis, chikungunya, bird flu- preventive measures during out breaks.
- Vaccines: Introduction to immunity, Fundamental concepts in vaccination and traditional methods of vaccine production (production of DPT and Rabies vaccine), Production of modern vaccines (production of Hepatitis Vaccine).
III.Data Interpretation and Problem Solving:
- Data Analysis – Analytical Interpretation of statistical Data, Study of Graphs and Charts – Bar graphs, Line graphs and Pie-charts and drawing conclusions.
- Problems based of Tabular and Diagrammatical Data – Problems based on Probability Logical Reasoning, Analytical and Mental ability.
- Quantitative Aptitude – Number Sequences, Series, Averages, Number Systems, Ratio and Proportion, Profit and Loss.
- Time and Work, Speed-Time-Distance, Simple Interest, Analytical and Critical reasoning.
- Decision Making and Problem Solving: A duly structured situation will be presented to the candidates and they will be asked to analyze and suggest their own solution to the problem arising out of situations.
TELANGANA MOVEMENT AND STATE FORMATION
I.The idea of Telangana (1948-1970):
- Historical Background: Telangana as a distinctive cultural unit in Hyderabad Princely State, its geographical, cultural, socio, political and economic features- People of Telangana- castes, tribes, religion, arts, crafts, languages, dialects, fairs, festivals and important places in Telangana. Administration in Hyderabad Princely State and Administrative Reforms of Salar Jung and Origins of the issue of Mulkis-Non-Mulkis; Employment and Civil Services Rules under Mir Osman Ali Khan, Vii Nizam's Farman of 1919 and Definition of Mulki – Establishment of Nizam's Subjects League known as the Mulki League 1935 and its Significance; Merger of Hyderabad State into Indian Union in 1948; Employment Policies under Military Rule an Vellodi, 1948-52 Violation of Mulki-Rules and Its Implications.
- Hyderabad State in Independent India- Formation of Popular Ministry under Burgula Ramakrishna Rao and 1952 Mulki-Agitation; Demand for Employment of Local people and City College Incident- Its importance. Justice Jagan Mohan Reddy Committee Report, 1953 – Initial debates and demand for Telangana State-Reasons for the Formation of States Reorganization Commission (SRC) under Fazal Ali in 1953-Main Provisions and Recommendations of SRC-Dr. B.R. Ambedkar's views on SRC and smaller states.
- Formation of Andhra Pradesh, 1956: Gentlemen's Agreement – its Provisions and Recommendations; Telangana Regional Committee, Composition, Functions and Performance – Violation of Safeguards-Migration from Coastal Andhra Region and its Consequences; Post-1970 Development Scenario in Telangana-Agriculture, Irrigation, Power, Education, Employment, Medical and Health etc.
- Violation of Employment and Service Rules: Origins of Telangana Agitation-Protest in Kothagudem and other places, Fast unto Death by Ravindranth; 1969 Agitation for Separate Telangana. Role of Intellectuals, Students, Employees in Jai Telangana Movement.
- Formation of Telangana Praja Samithi and course of Movement – the Spread of Telangana Movement – Major Events, Leaders and Personalities-All Party Accord – Go 36 – Suppression of Telangana Movement and its Consequences-The Eight Point and Five-Point Formulas-Implications.
II.Mobilisational phase (1971-1990):
- Court Judgements on Mulki Rules- Jai Andhra Movement and its Consequences- Six point Formula 1973, and its Provisions; Article 371-D, Presidential Order, 1975-Officers (Jayabharat Reddy) committee report –G.O 610 (1985) ; its provisions and violations Reaction and Representations of Telangana Employees
- Rise and Spread of Naxalite Movement, causes and consequences – Anti-Landlord Struggles in Jagityala-Siricilla, North Telangana; Rytu-Cooli Sanghams; Alienation of Tribal Lands and Adivasi Resistance-Jal, Jungle, and Zamin.
- Rise of Regional Parties in 1980's and Changes in the Political, Socio-Economic and Cultural fabric of Telangana- Notion of Telugu Jathi and suppression of Telangana identity- Expansion of new economy in Hyderabad and other parts of Telangana; Real Estate, Contracts, Finance Companies; Film, Media and Entertainment Industry; Corporate Education and Hospitals etc; Dominant Culture and its implications for Telangana self respect, Dialect, Language and Culture.
- Liberalization and Privatisation Policies in 1990's and their consequences – Emergence of regional disparities and imbalances in political power, administration, education, employment-Agrarian crisis and decline of Handicrafts in Telangana and its impact on Telangana Society and economy.
- Quest for Telangana identity-intellectual discussions and debates-political and ideological efforts-Growth of popular unrest against regional disparities, discrimination and under development of Telangana.
III.Towards Formation of Telangana State (1991-2014)
- Public awakening and Intellectual reaction against discrimination-formation of Civil society organization, Articulation of separate Telangana identity: Initial organisations raised the issues of separate Telangana; Telangana Information Trust-Telangana Aikya Vedika, Bhuvanagiri Sabha – Telangana Jana Sabha, Telangana Maha Sabha – Warangal Decleration – Telangana Vidyarthula Vedika; etc, Efforts of Telangana Congress & BJP in highlighting the issue.
- Establishement of Telangana Rashtra Samithi in 2001, Political Realignment and Electoral Alliances in 2004 and later Phase of Telangana Movement – TRS in UPA- Girgliani Committee-Telangana Employees Joint Action Committee – Pranab Mukherjee Committee- 2009-Elections-Alliances- Telangana in Election Manifestos- The agitation against Hyderabad as Free-zone – and Demand for separate Statehood- Fast-Unto-Death by K. Chandra Shekar Rao-Formation of Political Joint Action Committee (2009).
- Role of Political Parties-TRS, Congress, B.J.P., Left parties, T.D.P., M.I.M and other political parties such as Telangana Praja Front, Telangana United Front etc., Dalit-Bahujan Sanghams and Grass roots Movement organisations – Other Joint Action Committees and popular protests- Suicides for the cause of Telangana.
- Cultural Revivalism in Telangana, other symbolic expressions in Telangana Movement- Literary forms- performing arts and other cultural expressions- writers, poets, singers, intellectuals, Artists, Journalists, Students, Employees, Advocates, Doctors, NRIs, women Civil society group, organized and unorganized sectors, castes, communities and other social groups in Transforming the agitation into a mass movement – Intensification of Movement, Forms of Protest and Major events: Sakalajanula Samme, Non-Cooperation Movement; Million March, etc.,
- Parliamentary Process; UPA Government's stand on Telangana-All-Party Meeting-Anthony Committee- Statements on Telangana by Central Home Ministers – Sri Krishna Committee Report and its Recommendations, AP Assembly and Parliamentary proceedings on Telangana, Declaration of Telangana State in Parliament, Andhra Pradesh State Reorganization Act, 2014- Elections and victory of Telangana Rashtra Samithi and the first Government of Telangana State.
GROUP-II SERVICES
Paper-I: GENERAL STUDIES AND GENERAL ABILITIES:
- Current Affairs – Regional, National & International.
- International Relations and Events.
- General Science; India's Achievements in Science and Technology.
- Environmental Issues; Disaster Management – Prevention and Mitigation Strategies.
- World Geography, Indian Geography and Geography of Telangana State.
- History and Cultural Heritage of India.
- Society, Culture, Heritage, Arts and Literature of Telangana.
- Policies of Telangana State.
- Social Exclusion, Rights Issues and Inclusive Policies.
- Logical Reasoning; Analytical Ability and Data Interpretion.
- Basic English. (10th Class Standard)
PAPER-II: HISTORY, POLITY AND SOCIETY
I.Socio Cultural History of India and Telangana:
- Salient features of Indus Valley Civilizations; socity and culture – Early and later vedic civilizations; Religious Movements in Sixth Century B.C –Jainism and Buddhism. Socio, Cultural Contribution of Mauryas, Guptas, Pallavas, Chalukyas, Cholas Art and Architecture – Harsha and the Rajput Age.
- The Advent of Islam and the Establishment of Delhi Sultanate Socio, Cultural Conditions under the Sultanate –Sufi and Bhakti Movements. The Mughals: Social and Cultural Conditions; Language, Literature, Art and Architecture. Rise of Marathas and their contribution to Culture; Socio-Cultural conditions in the Deccan under the Bahamanis and Vijayanagara – Literature, Art and Architecture.
- Advent of Europeans: Rise and Expansion of British Rule: Socio-Cultural Policies – Cornwallis, Wellesley, William Bentinck, Dalhousie and others. The Rise of Socio-Religious Reform Movements in the Nineteenth Century. Social Protest Movements in India-Jotiba and Savithribai Phule, Ayyankali, Narayana Guru, Periyar Ramaswamy Naicker, Gandhi, Ambedkar etc.
- Socio-Cultural conditions in Ancient Telangana-Satavahanas, lkshvkus, Vishnukundins, Mudigonda and Vemulawada Chalukyas. Religion, Language, Literature, Art and Architecture; Medieval Telangana – Contribution of Kakatiyas, Rachakonda and Devarakonda Velamas, Qutub Shahis; Socio – Cultural developments: Emergence of Composite Culture. Fairs, Festivals, Moharram, Ursu Jataras etc.
- Foundation of Asaf Jahi Dynasty- from Nizam –ul Mulk to Mir Osaman Ali Khan – Salar Jung Reforms Social system and Social conditions-jagirdars, Zamindars, Deshmuks, and Doras- Vetti and Bhagela system and position of Women. Rise of Socio-Cultural Movements in Telangana: Arya Samaj, Andhra Maha Sabha, Andhra Mahila Sabha, Adi-Hindu Movements, Literary and Library Movements. Tribal and peasant Revolts: Ramji Gond, Kumaram Bheemu, and Telangana Peasant Armed Struggle – Police Action and the End of Nizam Rule.
II.Overview of the Indian Constitution and Politics:
- Evolution of Indian Constitution – Nature and salient features – Preamble.
- Fundamental Rights – Directive Principles of State Policy – Fundamental Duties.
- Distinctive Features of Indian Federalism – Distribution of Legislative and Administrative Power between Union and States.
- Union and State Governments – President – Prime Minister and Council of Ministers; Governor Chief Minister and Council of Ministers – Powers and Functions.
- Rural and Urban Governance with special reference to the 73rd and 74th Amendments.
- Electoral System Free and fair Elections, Malpractices; Election Commission; Electoral Reforms and Political Parties.
- Judicial System in India – Judicial Activism.
- (a).Special Provisions for Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes, Backward Classes, Women and Minorities.
(b).Welfare Mechanism for Enforcement – National Commission for Scheduled Castes, National Commission for Scheduled Tribes and National Commission for Backward Classes. - Indian Constitution: New Challenges.
III.Social Structure, Issues and Public Policies.
- Indian Social Structure :
Salient Features of Indian society: Caste, Family, Marriage, Kinship, Religion, Tribe Women Middle class – Socio-cultural Features of Telangana Society. - Social Issues:
Inequality and Exclusion: Casteism, Communalism, Regionalism, Violence against Women, Child Labour, Human trafficking, Disability and Aged. - Social Movements:
Peasant's Movements, Tribal movements, Backward Class Movements, Dalit Movements, Environmental Movements, Women's Movements, Regional Autonomy Movements, Human Rights Movements. - Telangana Specific Social Issues:
Vetti, Jogini, Devadasi System, Child labour, Girl child, Flourosis, Migration, Farmer's and Weaver's Distress. - Social Policies and Welfare Programmes:
Affirmative Policies for SCs, STs, OBC, Women, Minorities, Labour, Disabled and Children; Welfare Programmes: Employment, Poverty Alleviation Programmes; Rural and Urban, Women and Child Welfare, Tribal Welfare.
PAPER- III : ECONOMY AND DEVELOPMENT
I.Indian Economy: Issues and Challenges.
- Growth and Development : Concepts of Growth and Development-Relationship between Growth and Development.
- Measures of Economic Growth: National Income-Definition, Concepts and Methods of measuring National Income; Nominal and Real Income
- Poverty and Unemployment: Concepts of Poverty–Income based Poverty and Non-Income based Poverty; Measurement of Poverty; Unemployment- Definition, Types of Unemployment.
- Planning in Indian Economy: Objectives, Priorities, Strategies, and Achievements of Five Plans – 12th FYP; Inclusive Growth – NITI Aayog.
II.Economy and Development of Telangana
- Telangana Economy in undivided Andhra Pradesh (1956-2014)-Deprivations (Water (Bachavat Committee), Finances (Lalit, Bhargava, Wanchu Committees) and Employment (Jai Bharat Committee, Girgilan Committee) and Under Development.
- Land Reforms in Telangana: Abolition of Intermediaries: Zamindari, Jagirdari and Inamdari; Tenancy Reforms; Land ceiling; Land alienation in Scheduled Areas.
- Agriculture and Allied Sectors: Share of Agriculture and Allied sectors in GSDP; Distribution of land holding; Dependence on Agriculture; Irrigation-Sources of Irrigation; Problem of Dry land Agriculture; Agricultrual credit.
- Industry and Service Sectors: Industrial Development; Structure and Growth of Industry sector- Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSME) sector; Industrial Infrastructure; Industrial Policy of Telangana; Structure and Growth of Service sector.
III.Issues of Development and Change.
- Development Dynamics; Regional Inequalities in India - Social Inequalities – Caste, Ethnicity (tribe), Gender and Religion; Migration; Urbanisation.
- Development and Displacement: Land Acquisition Policy; Resettlement and Rehabilitation.
- Economic Reforms: Growth, Poverty and Inequalities – Social Development (education and health); Social Transformation; Social Security.
- Sustainable Development: Concept and Measurement; Sustainable Development Goals.
(TELANGANA MOVEMENT AND STATE FORMATION)
I.The idea of Telangana (1948-1970):
- Historical Background: Telangana as a distinctive cultural unit in Hyderabad Princely State, its geographical, cultural, socio, political and economic features- people of Telangana- castes, tribes, religion, arts, crafts, languages, dialects, fairs, festivals and important places in Telangana. Administration in Hyderabad Princely State ad Administrative Reforms of Salar Jung and Origins of the issue of Mulkis-Non-Mulkis; Employment and Civil Services Rules under Mir Osman Ali Khan, VII Nizam's Farman of 1919 and Definition of Mulki – Establishment of Nizam's Subjects League known as the Mulki League 1935 and its Significance; Merger of Hyderabad State into Indian Union in 1948- Employment policies under Military Rule and Vellodi, 1948-52; Violation of Mulki-Rules and Its Implications.
- Hyderabad State in Independent India- Formation of Popular Ministry under Burgula Ramakrishna Rao and 1952 Mulki-Agitation; Demand for Employment of Local people and City College Incident- Its importance. Justice Jagan Mohan Reddy Committee Report, 1953- Initial debates and demand for Telangana State-Reasons for the Formation of States Reorganization Commission (SRC) under Fazal Ali in 1953-Main Provisions and Recommendations of SRC-Dr. B.R. Ambedkar's views on SRC and smaller states.
- Formation of Andhra Pradesh, 1956: Gentlemen's Agreement – its Provisions and Recommendations; Telangana Regional Committee, Composition, Functions and Performance – Violation of Safeguards-Migration from Coastal Andhra Region and its Consequences-Post-1970 development Scenario in Telangana-Agriculture, Irrigation, Power, Education, Employment, Medical and Health etc.
- Violation of Employment and Service Rules: Origins of Telangana Agitation-Protest in Kothagudem and other places, Fast unto Death by Ravindranath; 1969 Agitation for Separate Telangana. Role of Intellectuals, Students, Employees in Jai Telangana Movement.
- Formation of Telangana Praja Samithi and Course of Movement – the Spread of Telangana Movement- Major Events, Leaders and Personalities- All Party Accord–Go 36–Suppression of Telangana Movement and its Consequences-The Eight Point and Five-Point Formulas-Implications.
II.Mobilisational phase (1971-1990):
- Court Judgements on Mulki Rules- Jai Andhra Movement and its Consequences- Six Point Formula 1973, and its Provisions; Article 371-D, Presidential Order, 1975-Officers (Jayabharat Rdddy) Committee Report- Go 610 (1985); its Provisions and Violation-Reaction and Representations of Telangana Employees.
- Rise and Spread of Naxalite Movement, causes and consequences–Anti-Landlord Struggles in Jagityala-Siricilla, North Telangana Ryto-Cooli Sanghams; Alienation of Tribal Lands and Adivasi Resistance- Jal, Jungle, and Zamin.
- Rise of Regional Parties in 1980's and Changes in the Political, Socio-Economic and Cultural fabric of Telangana-Notion of Telugu Jathi and suppression of Telangana identity- Expansion of new economy in Hyderabad and other parts of Telangana; Real Estate, Contracts; Corporate Education and Hospitals etc; Dominant Culture and its implications for Telangana self respect, Dialect, Language and culture.
- Liberalization and Privatisation policies in 1990's and their consequences – Emergence of regional disparities and imbalances in political power, administration, education employment-Agrarian crisis and decline of Handicrafts in Telangana and its impact on Telangana Society and economy.
- Quest for Telangana identity-Intellectual discussions and debates-Politial and ideological efforts-Growth of popular unrest against regional disparities, discrimination and under development of Telangana.
III.Towards Formation of Telangana State (1991-2014):
- Public awakening and Intellectual reaction against discrimination-formation of Civil society organization, Articulation of separate Telangana Identity; Initial organisations raised the issues of separate Telangana; Telangana Information Trust-Telangana Aikya Vedika, Bhuvanagiri Sabha- Telangana Jana Sabha, Telangana Maha Sabha-Wrangal Decleration-Telangana Vidyarthuala Vedika; etc, Efforts of Telangana Congress & BJP in highlighting the issues.
- Establishment of Telangana Rashtra Samithi in 2001, Political Realignment and Electoral Alliances in 2004 and later Phase of Telangana Movement – TRS in UPA- Girgliani Committee-Telangana Employees Joint Action Committee – Pranab Mukherjee Committee- 2009- Elections-Alliances- Telangana in Election Manifestos- The agitation against Hyderabad as Free-zone – and Demand for separate Statehood- Fast-Unto-Death by K. Chandra Shekar Rao-Formation of Political Joint Action Committee (2009).
- Role of Political Parties-TRS, Congress, B.J.P., Left parties, T.D.P., M.I.M and other political parties such as Telangana Praja Front, Telangana United Front etc., Dalit-Bahujan Sanghams and Grass roots Movement organisations – Other Joint Action Committees and popular protests- Suicides for the cause of Telengana.
- Cultural Revivalism in Telangana, other symbolic expressions in Telangana Movement- Literary forms- performing arts and other cultural expressions- writers, poets, singers, intellectuals, Artists, Journalists, Students, Employees, Advocates, Doctors, NRIs, women, Civil society groups, organized and unorganized sectors, castes, communities and other social group in transforming the agitationinto a mass movement-Intensification of Movement, Forms of Protest and Major events: Sakalajanula Samme, Non-Cooperation Movement; Million March, etc:
- Parliamentary Process; UPA Government's stand on Telangana-All-Party Meeting-Anthony Committee- Statements on Telangana by Central Home Minister–Sri Krishna Committee Report and its Recommendations, AP Assembly and Parliamentary proceedings on Telangana, Declaration of Telangana State in Parliament, Andhra Pradesh State Reorganization Act, 2014- Election and victory of Telangana Rashtra Samithi and the first Government of Telangana State.
GROUP-III SERVICES
SCHEME OF EXAMINATION
PAPER | SUBJECT | QUESTIONS (MULTIPLE CHOICE) | DURATION (HOURS) | MAXIMUM MARKS |
PART-A WRITTEN EXAMINATION (Objective Type) | ||||
Paper-I | GENERAL STUDIES AND GENERAL ABILITIES | 150 | 2 ½ | 150 |
Paper-II | HISTORY, POLITY AND SOCIETY
| 150(3×50) | 2 ½ | 150 |
Paper-III | ECONOMY AND DEVELOPMENT
| 150(3×50) | 2 ½ | 150 |
Total Marks | 450 | |||
GROUP-III SERVICES
PAPER-I: GENERAL STUDIES AND GENERAL ABILITIES
- Current Affairs – Regional, National & International.
- International Relations and Event.
- General Science; India's Achievements in Science and Technology.
- Environmental Issues; Disaster Management- Prevention and Mitigation Strategies.
- World Geography, Indian Geography and Geography of Telangana State.
- History and Cultural Heritage of India.
- Society, Culture, Heritage, Arts and Literature of Telangana.
- Policies of Telangana State.
- Social Exclusion, Rights Issues and Inclusive Policies.
- Logical Reasoning; Analytical Ability and Data Interpretation.
- Basic English (8th Class Standard)
(PAPER-II)
PAPER-II: HISTORY, POLITY AND SOCIETY
I.Socio-Cultural History of Telangana and Formation of Telangana State:
- Satavahanas, Ikshvakus, Vishnukundins, Mudigonnd and Vemulawada Chalukyas and their contribution to culture; Social System; Religious conditions; Buddhism and Jainism in Ancient Telangana; Growth of Language and Literature, Art and Architecture.
- The establishment of Kakatiya kingdom and their contribution to socio-cultural development. Growth of Telugu Language and Literature under the Kakatiyas – Art, Architecture and Fine Arts. Rachakonda and Deverakonda Velamas, Social and Religious Conditions; Growth of Telugu Language and Literature, Popular protest against Kakatiyas: Sammakka – Sarakka Revolt; Socio-Cultural contribution of Qutubshahis – Growth of Language, Literature, Art, Architecture, Festivals, Dance, and Music. Emergence of Composite Culture.
- Asaf Jahi Dynasty; Nizam-British Relations: Salarjung Reforms and its impact; Socio – Cultural – Religious Conditions under the Nizams: Educational Reforms, Establishment of Osmania University and Higher Education; Growth of Employment and the Rise of Middle Classes.
- Socio-cultural and Political Awakening in Telangana: Role of Arya Samaj-Andhra Mahasabha; Andhra Saraswatha Parishat, Literary and Library movements, Adi- Hindu movement, Andhra Mahila Sabh and the growth of Women's movement; Tribal Revolts, Ramji Gond and Kumaram Bheemu, - The Telangana Peasant Armed Struggle; Causes and Consequences.
- Integration of Hyderabad State into Indian Union and formation of Andhra Pradesh. Gentlemen Agreement; Mulki Movement 1952-56; Violation of Safeguards – Regional imbalances – Assertion of Telangana identity; Agitation for Separate Telangana State 1969-70 – Growth of popular protest against discrimination and movements towards the formation of Telangana State 1971-2014.
II.Overview of the Indian Constitution and Politics.
- Evolution of Indian Constitution – Nature and Salient Features – Preamble.
- Fundamental Rights – Directive Principles of State Policy – Fundamental Duties.
- Distinctive Features of Indian Federalism – Distribution of Legislative and Administrative Powers between Union and States.
- Union and State Governments – President – Prime Minister and Council of Ministers; Governor, Chief Minister and Council of Ministers – Powers and Functions.
- Rural and Urban Governance with special reference to the 73rd and 74th Amendments.
- Electoral System: Free and Fair Elections, Malpractices; Election Commission; Electoral Reforms and Political Parties.
- Judicial System in India – Judicial Activism.
- (a) Special Provisions for Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes, Backward Classes, Women and Minorities.
(b) Welfare Mechanism for Enforcement – National Commission for Scheduled Castes, National Commission for Scheduled Tribes and National Commission for Backward Classes. - Indian Constitution: New Challenges.
III.Social Structure, Issues and Public Policies.
- Indian social structure:
Salient Features of Indian society: Caste, Family, Marriage, Kinship, Religion, Tribe, Women, Middle class – Socio-Cultural Features of Telangana Society. - Social Issues:
Inequality and Exclusion: Casteism, Communalism, Regionalism, Violence against Women, Child Labour, Human Trafficking, Disability and Aged. - Social Movements:
Peasant's Movements, Tribal Movements, Backward Class Movements, Dalit Movements, Environmental Movements, Women's Movements, Regional Autonomy Movements, Human Rights Movements. - Telangana Specific Social Issues:
Vetti, Jogini, Devadasi System, Child labour, Girl Child, Flourosis, Migration, Farmer's and Weaver's Distress. - Social Policies and Welfare programmes:
Affirmative Policies for SCs, STs, OBC, Women, Minorities, Labour, Disabled and Children; Welfare Programmes: Employment, Poverty Alleviation Programmes; Rural and Urban, Women and Child Welfare, Tribal Welfare.
PAPER-III: ECONOMY AND DEVELOPMENT
I.Indian Economy: Issues and Challenges:
- Growth and Development: Concepts of Growth and Development-Relationship between Growth and Development.
- Measures of Economic Growth: National Income- Definition, Concepts and Methods of measuring National Income; Nominal and Real Income.
- Poverty and Unemployment: Concepts of Poverty – Income based Poverty and Non-Income based Poverty; Measurement of Poverty; Unemployment- Definition, Types of Unemployment.
- Planning in Indian Economy: Objectives, Priorities, Strategies, and Achievements of Five year Plans – 12th FYP; Inclusive Growth – NITI Aayog.
II.Economy and Development of Telangana:
- Telangana Economy in undivided Andhra Pradesh (1956-2014)- Deprivations (Water (Bachavat Committee), Finances (Lalit, Bhargava, Wanchu Committees) and Employment (Jai Bharat Committee, Girgilan Committee) and Under Development.
- Land Reforms in Telangana: Abolition of Intermediaries: Zamindari, Jagirdari and Inamdari; Tenancy Reforms; Land ceiling; Land alienation in Scheduled Areas
- Agriculture and Allies Sectors: Share of Agriculture and Allied sectors in GSDP; Distribution of land holdings; Dependence on Agriculture; Irrigation-Sources of Irrigation; Problems of Dry land Agriculture; Agricultural credit .
- Industry and Service Sectors: Industrial Development; Structure and Growth of Industry sector- Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSME) Sector; Industrial Infrastructure; Industrial Policy of Telangana; Structure and Growth of Service sector.
III.Issues of Development and Change.
- Development Dynamics: Regional Inequalities in India – Social Ineaualities – Caste, Ethnicity (tribe), Gender and Religion; Migration; Urbanisation.
- Development and Displacement: Land Acquisition Policy; Resettlement and Rehabilitation.
- Economic Reforms: Growth, Poverty and Inequalities – Social Development (education and health); Social Transformation; Social Security.
- Sustainable Development: Concept and Measurement; Sustainable Development Goals.
Group -4
Paper – 1General knowledge
- Current affairs
- International Relations and Events.
- General Science in everyday life.
- Environmental Issues and Disaster Management.
- Geography and Economy of India and Telangana.
- Indian Constitution: Salient Features.
- Indian Political System and Government.
- Modern Indian History with a focus on Indian National Movement.
- History of Telangana and Telangana Movement.
- Society, Culture, Heritage, Arts and Literature of Telangana.
- Policies of Telangana State.
PAPER-II: SECRETARIAL ABILITIES
- Mental Ability. (Verbal and non-verbal)
- Logical Reasoning
- Comprehension
- Re-arrangement of sentences with a view to improving analysis of a passage.
- Numerical and Arithmetical abilities.
PAPER-I: GENERAL STUDIES AND GENERAL ABILITIES
- Current affairs – Regional, National and International.
- International Relations and Event.
- General Science; India's Achievements in Science and Technology.
- Environmental issues; Disaster Management- Prevention and Mitigation Strategies.
- Economic and Social Development of India and Telangana.
- Physical, Social and Economic Geography of India.
- Physical, Social and Economic Geography and Demography of Telangana.
- Socio-economic, Political and Cultural History of Modern India with special emphasis on Indian National Movement.
- Socio-economic, Political and Cultural History of Telangana with special emphasis on Telangana Statehood Movement and formation of Telangana state.
- Indian Constitution; Indian Political System; Governance and Public Policy.
- Social Exclusion; Rights issues such as Gender, Caste, Tribe, Disability etc. and inclusive policies.
- Society, Culture, Heritage, Arts and Literature of Telangana.
- Policies of Telangana State.
- Logical Reasoning; Analytical Ability and Data Interpretation.
- Basic English. (10th Class Standard)
PAPER-II: CONCERNED SUBJECT
(Detailed syllabus will be displayed at the time of Notification)
(PAPER-I: GENERAL STUDIES AND GENERAL ABILITIES)
- Current Affairs – Regional, National and International.
- International Relations and Events.
- General Science; India's Achievements in Science and Technology.
- Environmental issues and Disaster Management.
- Economy of India and Telangana.
- Geography of India with a focus on Telangana.
- Indian Constitution and Polity with a focus on local self Government.
- Society, Culture, Heritage, Arts and Literature of Telangana.
- Policies of Telangana State.
- History of Modern India with a focus on Indian National Movement.
- History of Telangana with special emphasis on Movement for Telangana Statehood.
- Logical Reasoning; Analytical Ability and Data Interpretation.
- Basic English. (8th Class Standard)
PAPER-II: CONCERNED SUBJECT
(Detailed syllabus will be displayed at the time of Notification)
SYLLABUS FOR PRELIMINARY WRITTEN TEST
ARITHMETIC & TEST OF REASONING/MENTAL ABILITY (OBJECTIVE TYPE) (100 QUESTIONS)
Arithmetic: It will include questions on problems relating to number system, simple Interest, compound interest, ratio & proportion, average, percentage, profit & loss, time & work, work & wages, time & distance, clocks & calendars, partnership, mensuration etc.
Test of Reasoning: It will include questions of both verbal & non-verbal type and questions on analogies, similarities, and differences, spatial visualization, spatial orientation, problem solving, analysis, judgment, decision making, visual memory etc.
GENERAL STUDIES (OBJECTIVE TYPE) (100 QUESTIONS)
- General Science – contemporary developments in science and technology and their implications including matters of everyday observation and experience, contemporary issues relating to protection of environment as may be expected of a well educated person who has not made a special study of any scientific discipline.
- Current events of national and international importance.
- History of India (including Indian National Movement) – emphasis will be on broad and general understanding of the subject in its social, economic, cultural and political aspects.
- (Geography of India).
- Indian Polity and Economy – including the Country's political system, rural development, planning and economic reforms in India.
- Telangana Movement and State Formation – The idea of Telangana (1948-1970), Mobilization phase (1971-1990), towards formation of Telangana State (1991-2014)
SYLLABUS FOR FINAL WRITTEN EXAMINATION
PAPER-I: ENGLISH (OBJECTIVE TYPE) (200 QUESTIONS)
ARITHMETIC & TEST OF REASONING/MENTAL ABILITY (OBJECTIVE TYPE) (100 QUESTIONS)
Arithmetic: it will include questions on problems relating to number system, simple interest, compound interest, ratio & proportion, average, percentage, profit & loss, time & work, work & wages, time & distance, clocks & calendars, partnership, mensuration etc
Test of Reasoning: It will include questions of both verbal & non-verbal type and questions on analogies, similarities and differences, spatial visualization, spatial orientation, problem solving, analysis, judgment, decision making, visual memory etc
GENERAL STUDIES (OBJECTIVE TYPE) (100 QUESTIONS)
- General Science – contemporary developments in science and technology and their implications including matters of everyday observation and experience, contemporary issues relating to protection of environment as may be expected of a well educated person who has not made a special study of any scientific discipline.
- Current events of national and international importance.
- History of India (including Indian National Movement) – emphasis will be on broad and general understanding of the subjects in its social, economic, cultural and political aspects.
- Geography of India .
- Indian Polity and Economy – including the Country's political system, rural development, planning and economic reforms in India.
- Telangana Movement and State Formation – The idea of Telangana (1948-1970), Mobilization phase (1971-1990), towards formation of Telangana State (1991-2014) .
Qualifying Paper in English will be of Matriculation or equivalent standard. Questions of the standard of SSC/Matriculation seeking to ascertain the Candidate's knowledge of Usage, Vocabulary, Grammar, Comprehension and other language skills will be asked for in the Objective Format.
Paper-4
Candidates have to choose one of the language i.e., either Telugu or Urdu and should Indicate their choice as and when asked for by the recruiting authority. Option once exercised will be final and a candidate will not be allowed to change it subsequently.
Qualifying Paper in Telugu or Urdu will be of Matriculation or equivalent standard. Questions of the Standard SSC/Matriculation seeking to ascertain the Candidate's knowledge of Usage, Vocabulary, Grammar, Comprehension and other language skills will be asked for in the Objective Format.
FOR THE POST OF SCT PC CIVIL AND/OR EQUIVALENT
FOR PRELIMINARY WRITTEN TEST
(INTERMEDIATE STANDARD – OBJECTIVE TYPE - 200 QUESTIONS)
- English
- Arithmetic
- General Science
- History of India, Indian culture, Indian National Movement.
- Indian Geography, Polity and Economy.
- Current events of national and international importance.
- Test of Reasoning/Mental Ability.
- Contents pertaining to the State of Telangana.
FOR FINAL WRITTEN EXAMINATION
(INTERMEDIATE STANDARD – OBJECTIVE TYPE – 200 QUESTIONS)
- English
- Arithmetic
- General Science
- History of India, Indian culture, Indian National Movement.
- Indian Geography, Polity and Economy
- Current events of national and international importance
- Test of Reasoning/Mental Ability
- Contents pertaining to the State of Telangana
- Personality test the question will be from Ethics, Sensitivity to Gender and weaker sections, social awareness, Emotional Intelligence.
The Preliminary Examination shall consist of two compulsory paper, namely, General studies-I of 200 marks and General Studies-II of 200 marks. The question papers shall be multiple choices, objective type. The question papers will be set both in Hindi and English.
General Studies-I
Total Marks: 200Time: 2 hours
The paper will consist of 100 objective type questions, each of 2 marks, drawn from the subjects listed below. Candidates will have to answer all the questions.
(A)History of India:15 Questions
1.Ancient India (5 questions)
2.Medieval India (5 questions)
3.Modern India (5 questions)
(B)Geography of India:10 Questions
1.General Geography (3 questions)
2.Physical Geography (3 questions)
3.Economical Geography (2 questions)
4.Social & Demographic Geography (2 questions)
(C)Indian Polity and Governance:10 Questions
1.Constituton of India (4 Questions)
2.Public Administration and Good Governance (4 questions)
3.Decentrealization: Panchayats & Municipalities (2 questions)
(D)Economic and Sustainable Development:10 Questions
1.Basic features of Indian Economy (4 questions)
2.Sustainable Development and Economic issues (4 questions)
3.Economic Reforms and Globalization (2 questions)
(E)Science & Technology:15 Questions
1.General Science (6 questions)
2.Agriculture & Technology Development (6 questions)
3.Information & Communication Technology (3 questions)
(F)Jharkhand Specific Questions (General Awareness of its History, Society,
Culture & Heritage):10 Questions
(G)National & International Current Events:15 Questions
(H)General Questions of Miscellaneous nature, not requiring subject 15 Questions
specialization, such as,:
1.Human Rights
2.Environmental Protection, Bio-diversity & Climate Change
3.Urbanization
4.Sports
5.Disaster Management
6.Poverty and Un-employment
7.Awards
8.United Nations and other International Agencies
झारखण्ड लोक सेवा आयोग, प्रारंभिक परीक्षा
सामान्य अध्ययन पत्र - II
पूर्णांकः 200समयः 2 घण्टे
इस पत्र में 100 बहुवैकल्पिक/वस्तुपूरक (Objective types) प्रश्न होंगे। प्रत्येक प्रश्न 2 अंक का होगा। सभी प्रश्नों का उत्तरदेना अनिवार्य होगा।
A. झारखण्ड का इतिहास 8 प्रश्न 8 × 2 = 16
(क)मुण्डा शासन व्यवस्था - (1 प्रश्न)
(ख)नागवंशी शासन व्यवस्था - (1 प्रश्न)
(ग) पडहा पंचायत शासन व्यवस्था - (1 प्रश्न)
(घ) मांझी परगना शासन व्यवस्था - (1 प्रश्न)
(ड़) मुण्डा मानकी शासन व्यवस्था - (1 प्रश्न)
(च) दौकली सोहोर शासन व्यवस्था - (1 प्रश्न)
(छ)जातीय पंचायत शासन व्यवस्था - (2 प्रश्न)
B. झारखण्ड आन्दोलन 7 प्रश्न 7 × 2 = 14
(क)झारखण्ड के सदान - (1 प्रश्न)
(ख)झारखण्ड के आदिवासी - (1 प्रश्न)
(ग) झारखण्ड के स्वतंत्रता सेनानी - (1 प्रश्न)
(घ) झारखण्ड के विभूति - (2 प्रश्न)
(ड़) झारखण्ड आन्दोलन एवं राज्य गठन - (2 प्रश्न)
C. झारखण्ड की विशिष्ट पहचान 5 प्रश्न 5 × 2 = 10
(क)झारखण्ड की सामाजिक स्थिति - (1 प्रश्न)
(ख)झारखण्ड की सांस्कृतिक स्थिति - (1 प्रश्न)
(ग) झारखण्ड की राजनीतिक स्थिति - (1 प्रश्न)
(घ) झारखण्ड की आर्थिक स्थिति - (1 प्रश्न)
(ड़) झारखण्ड की धार्मिक विशिष्टताएं एवं पहचान - (1 प्रश्न)
D. झारखण्ड का लोक साहित्य, नृत्य, संगीत, वाद्य, दर्शनीय स्थल एवं आदिवासी संस्कृति
5 प्रश्न 5 × 2 = 10
(क)लोक साहित्य - (1 प्रश्न)
(ख)पारंपरिक कला एवं लोक नृत्य - (1 प्रश्न)
(ग) लोक संगीत एवं वाद्य - (1 प्रश्न)
(घ) दर्शनीय स्थल-प्राकृतिक, पुरातात्विक, ऐतिहासिक, धार्मिक एवं आधुनिक स्थल - (1 प्रश्न)
(ड़) आदिवासी-जाति-प्रजाति एवं विशेषताएं - (1 प्रश्न)
E. झारखण्डी साहित्य और साहित्यकार5 × 2 = 10
झारखंडी साहित्य एवं साहित्यकार - (5 प्रश्न)
F. झारखण्ड के प्रमुख शिक्षण संस्थान3 × 2 = 6
प्रमुख शिक्षण संस्थान - (3 प्रश्न)
G. झारखण्ड के खेल-कूद - (5 प्रश्न)5 × 2 = 10
H. झारखण्ड के भूमि संबंधी कानून/अधिनियम12 × 2 = 24
(क)छोटानागपुर काश्तकारी अधिनियम (C.N.T.) - (5 प्रश्न)
(ख)संताल परगना काश्तकारी अधिनियम (S.P.T.) - (5 प्रश्न)
(ग) अन्य राज्य परक अधिनियम - (2 प्रश्न)
I.1947 से राज्य में आर्थिक विकास का इतिहास झारखण्ड का भूगोल- जंगल, नदी,
पहाड़-पर्वत, खान-खनिज आदि - (10 प्रश्न)10 × 2 = 20
J.झारखण्ड की औद्योगिक नीति, विस्थापन और पुनर्वास नीति एवं अन्य नीतियां - (6 प्रश्न)6 × 2 = 12
K. झारखण्ड के प्रमुख उद्योग का नाम और स्थान तथा औद्योगिक विकास - (5 प्रश्न)5 × 2 = 10
L. झारखण्ड की प्रमुख योजनाएं एवं उपयोजनाएं - (5 प्रश्न)5 × 2 = 10
M. झारखण्ड में जंगल प्रबंधन एवं वन्य जीव जंतु संरक्षण कार्य - (5 प्रश्न) 5 × 2 = 10
N. झारखण्ड राज्य के पर्यावरण संबंधी तथ्य, हो रहे पर्यावरण परिवर्तन एवं उसके अपशमन (Mitigation) एवं अनुकूलन (Adaptation) संबंधी विषय - (7 प्रश्न)7 × 2 = 14
O. झारखण्ड में आपदा प्रबंधन - (5 प्रश्न)5 × 2 = 10
P. झारखण्ड से संबंधित विविध तथ्यों एवं समसामयिक घटनाएं - (7 प्रश्न)7 × 2 = 14
परिशिष्ट - 1(ख)
syllabus for the main examination of the jharkhand civil services
The Main Examination shall consist of six compulsory papers, common to all candidates two of these papers namely paper-I 100 Marks and Paper -II 150 Marks, shall be language based and the remaining four Papers each of 200 Marks shall be subject based. The language based papers shall be (i) A composite paper of General Hindi & General English and (ii) A Language & Literature Paper of certain selected languages of which every candidate will have to opt for one. The subject based Papers shall be (i) Social Science (History and Geography), (ii) Indian Constitution, Polity, Public Administration and Good Governance, (iii) Indian Economy, Globalization and Sustainable Development and (iv) General Science, Environment and Technology Development
The detailed syllabi of all the above six papers shall be as follows:
paper-I
General Hindi and General English
Total Marks : 100Time: 3 hours
The General Hindi and General English paper shall be a composite paper, consisting of two segments, namely. (i) Hindi and (ii) English. Both the segments shall be of equal weightage i.e. each of 50 marks. The purpose of the paper is to test the working knowledge of the candidates in the above two languages. As such the questions to be asked in both the segments of this paper shall be of matric standard only and shall be confined to the following areas-
(A)General Hindi: 50 marks
(क)निबंध (400 शब्दों का) - 15 अंक
(ख)व्याकरण - 15 अंक
(ग)वाक्य विन्यास - 10 अंक
(घ)संक्षेपण - 10 अंक
(B)General English : 50 marks
1.Essay (400 words)– 15 marks
2.Grammar– 15 marks
3.Comprehension– 10 marks
4.Precis– 15 marks
It will be only a qualifying paper in which out of 100 (combined both Hindi and English) every candidate will have to secure only 30 marks. Thus inclusion of 50 marks General English
component will not adversely impact the chances of students from Hindi/Regional Language background.
Paper-II
Language & Literature
Total Marks : 150Time: 3 hours
The candidates will have the choice to opt for one of the following languages & literature-
(i)Oriyya Language & Literature
(ii)Bangali Language & Literature
(iii)Urdu Language & Literature
(iv)Sanskrit Language & Literature
(v)English Language & Literature
(vi)Hindi Language & Literature
(vii)Santhali Language & Literature
(viii)Panchpargania Language & Literature
(ix)Nagpuri Language & Literature
(x)Mundari Language & Literature
(xi)Kurux Language & Literature
(xii)Kurmali Language & Literature
(xiii)Khortha Language & Literature
(xiv)Khadia Language & Literature
(xv)Ho Language & Literature
This paper will be set for a maximum of 150 Marks and marks obtained in this paper shall be counted for preparation of the Gradation-List of the Main Examination.
The detailed syllabi of the above 15 Languages & Literatures shall be as follows-
उडि़या पाठ्यक्रम
(For JPSC Main Examination)
पूर्ण संख्याः 150समय: 3 घंटा
खण्ड - क (75 Marks)
1. भाषा
(i) ओडि़या भाषा की उत्पत्ति और क्रम विकाश
(ii) ओडि़या अभिलेख का ऐतिहासिक और भाषा तात्विक अध्ययन
(iii)ओडि़या भाषा का मानकीकरण एवं व्याकरणिक संरचना
(iv)ओडिया लिपि उत्पत्ति और क्रम विकास
(v) ओडि़या भाषा के ऊपर अन्य भाषाओं का प्रभाव
2. व्याकरण
विशेष्य, विशेषण, सर्वनाम, लिंग, वचन, पुरुष, कारक, विभक्ति, अव्यय, क्रिया, संधि, समास, रूढि प्रयोग, विपरीतार्थक शब्द।
अलंकार- अनुप्रास, यमक, श्लेष, उपमा, उत्प्रेक्षा, व्यतिरेक, विभावना, विशेषोक्ति
3. ओडि़या साहित्य का इतिहास
(i) विभिन्न युग में ओडि़या पद्य साहित्य की प्रमुख प्रवृत्तियां
(ii) ओडि़या गद्य साहित्य का क्रमविकास - शिलालेख के गद्य से आधुनिक गद्य साहित्य तक।
(iii)ओडि़या उपन्यास साहित्य का उद्भव और क्रमविकास।
(iv)ओडि़या नाट्य साहित्य का उद्भव और क्रमविकास।
खण्ड - ख (75 Marks)
4. पद्य साहित्य
(i) जगन्नाथ दास ‘श्रीमद् भगवत’ एकादश स्कन्द (प्रथम पांच सर्ग)
(ii) दिनकृष्ण दास ‘‘रसकल्लोल’’ (छन्द संख्या 1, 2, 5, 33 और 34)
(iii)गंगाधर मेहेर - तपस्विनी
(iv)गोपबंधू दास - कारा-कविता
(v) सच्चिदानन्द राउतराय वाजिराउत
5. गद्य साहित्य
(i) फकीर मोहन सेनापति-छमाण आठगुणु
(ii) गोपिनाथ महन्ति-परजा
(iii)कालिन्दी वरण पाणिग्राही- गाटिर मणिष
(iv)फकीर मोहन सेनापति- गल्प स्वल्प (प्रथम भाग)
6. निबंध
समसामयिक समस्या विषय पर ओडि़या भाषा (देवनागरी लिपि) में निबंध लेखन
7. नाट्य साहित्य
(i) अश्विनी कुमार घोष-कोणार्क
(ii) रामचन्द्र मिश्र-घर संसार
(iii)गोपाल छोटराय- भरसा
8. आलोचना
(i) सरला साहित्य में समाजचित्र
(ii) रीतिकवि अभिमन्यु सामन्त शिहार
(iii)रोमांटिक कवि राधानाथ राय
(iv)फकीर मोहन सेनापति
(v) जातिय कवि गोपबंधु
9. संक्षेपण
JPSC Mains, Paper-II
Bangali Language & Literature
Marks : 150Time: 3 hours
part-I
(a)History of Bengali Language
(i)Origin and development of Bengali language
(ii)Origin and development of Bengali Script
(iii)Origin and development of old Aryan, Middle Indo Aryan, Modern Indo Bengali Language
(iv)The chronological track from Proto Indo-European to Bangla (Family tree with branches and approximate dates.)
(b)Bengali Upa- Bhasha Shabda Bhandar, Dwani Paribartaner sutra.
(c)History of Bengali Literature
(i)Charyapada
(ii)Andhakar yug
(iii)Krittibas
(iv)Maladhar Basu
(v)Sri krishna kirtan o chandidas
(vi)Bidyapati
Part-II
(d)Prose, Poetry, Drama
(i)Meghnad Vada Kabya- Madhusudan Dutta
(ii)Muchiram gurer Jibancharit- Bankimchandra
(iii)Achalayatam- Rabindranath
(iv)Srikanta (vol-1)- Saratchandra.
(v)Vaishnava padavali (Calcutta University), poems of Vidyapati, Chandidas, Jnanadas, Giovinddas and Balramdas.
(e)Grammar
(i)Bhabsamprasaran
(ii)Sarangsha
(iii)Pratibedan
(f)Development of Prose, Poetry, Drama, Critic and Novel in Bangla literature.
(g)Fiction major author (Bankimchandra, Tagore, Saratchandra, Bibhutibusan, Tarashanar, Manik)
Jharkhand Public Service Commission, Mains Paper-II
Urdu Literature
Marks: 150Time: 3 Hours
Part-I
(a)Different theories about the origin of Urdu language.
(b)Origin and development of Urdu script.
(c)Benefits of Linguistic.
(d)Urdu literature (prose fiction)
(i)Nirmala (Novel)-Premchand
(ii)Short stories
Baloo Bhangi-Krishna Chandra
Laj Wanti-Rajinder Singh Bedi
Khol Do-Saadat Hassan munto
Parinda Pakarnewali Gadi-Ghayas Ahamed Gaddi
Mrs. John-Sheen Akhtar
Part-II
(e)Urdu Poetry
Ghalib: - Ghazal
(i)Hazaron Khawahisen Aaisi ke.
(ii)Ye Na Thi hamari Qismat.
Meer taqi Meer:
(i)Ulti hogai sab tadbeeren
(ii)Shaam se kuch bujha sa Rahta.
Hasrat Mohani:
Chupke Chupke rat din Asnsoo bahana yaad hai.
(f)Following five poems:
(i)Lenin Khuda ke huzoor mein-Iqbal
(i)Saqui Nama-Iqbal
(iii)Naseehat Akhlaque-Akbar Allahabadi
(iv)Balai Zamini-Wahab danish
(v)Ertaqua-Jameel Muzhari
(g)Urdu Language (Grammar)
(i)Opposite
(ii)Gender
(iii)Letter
(iv)Application
(v)Meanings
(vi)Singular-Plural
(vii)Summary
झारखण्ड लोक सेवा आयोग, मुख्य परीक्षा पत्र-II
संस्कृत भाषा एवं साहित्य
पूर्णांकः 150समयः 3 घण्टा
खण्ड-I
(क) भाषा विज्ञानः संस्कृत भाषा का उद्भव और विकास (भारोपीय से लेकर मध्य आर्य भाषाओं तक) भाषा की उत्पत्ति के सिद्धान्त, ध्वनि-विज्ञान, पद विज्ञान, वाक्य विज्ञान, अर्थ विज्ञान, अर्थ-परिवर्तन और उनके कारण।
(ख) वैदिक संस्कृत साहित्य का इतिहासः वैदिक संहिताएं, ब्राह्मण ग्रंथ, आरण्यक तथा उपनिषद।
(ग) लौकिक संस्कृत साहित्य का इतिहासः पुराण साहित्य, रामायण, महाभारत तथा परवर्ती संस्कृत साहित्य (महाकाव्य नाटक, गद्य साहित्य, चम्पू)
(घ) संस्कृत व्याकरणः संस्कृत ध्वनियां, स्वर एवं व्यंजन, संधि, समास, कारक, उपपद विभक्ति, नामधातु कृत प्रत्यय, तद्धित प्रत्यय, स्त्री प्रत्यय।
खण्ड-II
(ड़) संस्कृत में निबंध लेखन।
(च) भारतीय दर्शनों का सामान्य परिचय, आस्तिक एवं नास्तिक दर्शन, वेदान्त दर्शन, सांख्य दर्शन, बौद्ध दर्शन।
(छ)भारतीय संस्कृति एवं इसकी विशेषताएं, वर्णाश्रम व्यवस्था, संस्कार।
(ज)वाल्मीकि रामायण (किष्किन्धा काण्ड), रघुवंश (सर्ग-6, श्लोक-1-20), श्री मद्भगवद्गीता (द्वितीय अध्याय), किरातार्जुनीयम (सर्ग-1), कादम्बरी (शुकनाशोपदेश), मृच्छ कटिक (प्रथम अंक), उत्तर रामचरितम (तृतीय अंक)।
JPSC Mains, Paper-II
English Language and Literature
Full Marks: 150Time: 3 Hours
Part-I
(a)History of English Language:
(i)Indo-European Family of Language
(ii)Teutonic Verbal system, Teutonic Accent
(iii)The First Sound Shifting or Grimm's Law
(iv)Old English (Dialects of Old English, Characteristics of Old English, Old English Vocabulary)
(v)Middle English (Dialects of Modern English, Characteristics of Middle English, Rise of Standard English)
(b)The Definition of Poetry: Its characteristics, purpose, forms of poetry -- lyric, sonnet, ode, balled, free verse, blank verse, rhymed verse, poetic terms--alliteration, resonance, rhyme scheme meter-- its types.
(c)Comprehension (A passage containing approximately 1000 words to be set):
(d)Grammar
(i)Noun, Verb, Adjective, Adverb, Article, Preposition, Subject-verb Agreement, Narration, Voice, Transformation, Clause.
(ii)Single-word substitution
(iii)Correction of errors
(iv)Pairs of words
(v)Idioms and Phrases
Part-II
English Literature:
(e)History of English Literature (British, American, Colonial and post-Colonial Writing) from the 14th century up to the 21st century:
Poetry, Drama, Prose, Novel, Criticism, Biography, Autobiography, Short-stories (General
introduction of eminent poets, dramatists, novelists, prose-writers, short-story writers, autobiographers, biographers, popular writers)
(f)Fiction and Drama (Critical Study and Explanation):
(i)Kanthapura Raja Rao
(ii)A Passage to India: E. M. Forster
(iii)Macbeth: William Shakespeare
(iv)Arms and the Man: G.B. Shaw
(g)Poetry (Critical Study and Explanation):
(i)The Quality of Mercy: William Shakespeare
(ii)The Little Black Boy: William Blake
(iii)The Solitary Reaper: William Wordsworth
(iv)Mutability: P.B. Shelley
(v)I Think Continually of Those Who were Truly Great
(vi)Heaven of Freedom: Rabindranath Tagore
(vii)A Soul's Prayer: Sarojini Naidu
(h)Prose (Critical Study and Explanation):
(i)On Habits: A.G. Gardiner
(ii)India Again: E.M. Forster
(iii)Playing the English Gentleman: Mahatma Gandhi
(iv)Of Studies: Francis Bacon
(v)Mr. Know All: Somerset Maugham
(vi)The Homecoming: Rabindranath Tagore
(vii)The Cherry Tree: Ruskin Bond
(i)Essay: On socio-economic or current topic
हिन्दी भाषा एवं साहित्य
झारखण्ड लोक सेवा आयोग मुख्य परीक्षा, पत्र-II
समयः 3 घंटापूर्णांकः 150
खण्ड-I
क. हिन्दी भाषा का इतिहासः हिन्दी का उद्भव और विकास, अपभ्रंश, अवहट्ट, पुरानी हिन्दी, भाषा परिवार, भाषा परिवार का वर्गीकरण, ध्वनि विज्ञान, देवनागरी लिपि का उद्भव और विकास, देवनागरी लिपि के गुण एवं दोष, शब्द-शक्ति, शब्द भंडार, बोलचाल की भाषा, रचनात्मक भाषा, राष्ट्रभाषा, राजभाषा, संपर्क भाषा के रूप में हिन्दी।
ख. काव्य शास्त्रः काव्य की परिभाषा, काव्य के लक्षण, काव्य हेतु, काव्य प्रयोजन, साधारणीकरण, रक्ष, छंद अलंकार।
ग. प्रयोजनमूलक हिन्दीः प्रयोजनमूलक हिन्दी, कार्यालयी हिन्दी, जनसंचार भाषा के रूप में हिन्दी, व्यावसायिक हिन्दी।
घ. व्याकरणः संज्ञा, सर्वनाम, क्रिया, विशेषण, कारक, समास, मुहावरे, उक्तियां, संधि विच्छेद, अनेकार्थक शब्द
खण्ड-II
क. हिन्दी साहित्य का इतिहासः हिन्दी साहित्येतिहास लेखन की समस्या एवं परम्परा साहित्येतिहास दर्शन, काल विभाजन, आदिकाल, भक्तिकाल, रीतिकाल, आधुनिक काल, छायावाद, प्रगतिवाद, प्रयोगवाद, नई कविता, गद्य का उद्भव और विकास, कहानी, उपन्यास, नाटक, एकांकी, आलोचना, निबंध, संस्मरण, रेखाचित्र, रिपोर्टज, आत्मकला, जीवनी का उद्भव एवं विकास, प्रमुख कवियों, कहानीकारों, उपन्यासकारों, नाटककारों, आलोचकों की रचनाओं का सामान्य परिचय
ख. आलोचनात्मक और व्याख्यात्मक
कबीर- कबीर ग्रंथावली सं- श्यामसुन्दर दास - प्रारंभिक 50 साखी
सूरदास-भ्रमरगीत-सं- रामचन्द शुक्ल - प्रारंभिक 50 पद
तुलसीदास - रामचरितमानस - अयोध्याकाण्ड
बिहारी-बिहारी रत्नाकर
संपादक- जगन्नाथ दास रत्नाकर, दोहा संख्याः 1, 38, 67, 70 112, 121, 154, 191, 192, 201
जयशंकर प्रसाद-कामायनी-श्रद्धा सर्ग
निराला-राम की शक्तिपूजा
अज्ञेय-कितनी नावों में कितनी बार
दिनकर-कुरुक्षेत्र (पहला सर्ग)
मुक्तिबोध-अंधेरे में (भाग एक)
ग- आलोचनात्मक और व्याख्यात्मकः
नाटक
भारतेन्दु हरिशचन्द्र-भारत दुर्दशा
जयशंकर प्रसाद-चन्द्रगुप्त
मोहन राकेश-आधे-अधूरे
उपन्यास
प्रेमचन्द-गोदान
फणीश्वरनाथ रेणु-मैला आंचल
श्री लाल शुक्ल-राग दरबारी
कहानी
प्रेमचन्द्र-कफन, ईदगाह, बूढ़ी काकी एवं नमक का दारोगा
जैनेन्द्र कुमार-पाजेब
जयशंकर प्रसाद-गुंडा
यशपाल-अभिशप्त
भीष्म साहनी-चीफ की दावत
उषा प्रियवंदा-वापसी
ज्ञान रंजन-पिता
ओम प्रकाश बाल्मीकि-यह अन्त नहीं
चन्द्रधर शर्मा गुलेरी-उसने कहा था
घ- निबंधः समसामयिक, सामाजिक, राजनीतिक, प्राकृतिक विषय पर निबंध लेखन
JPSC Mains Paper-II
Santali language-literature
संथाली भाषा-साहित्य
Full Marks: 150Time: 3 Hours
खण्ड-I
भाग-(क)
(i) संथाली भाषा का उद्भव और विकास।
(ii) संथाली भाषा की विशेषताएं।
(iii) संथाली भाषा का व्याकरण- संज्ञा, सर्वनाम, वचन, पुरुष, लिंग, काल, क्रिया, विशेषण, उपसर्ग एवं प्रत्यय, कारक, जीव अव्यय।
(iv)शब्द गठन, वाक्य संरचना एवं क्षेत्रीय रूप।
(v) लिपि का उद्भव, विशेषताएं, विकास।
(vi)संथाली भाषा के सहोदर भाषाएं एवं संबंध।
भाग - (ख) संथाली लोक साहित्य
(i) संथाली लोक साहित्य का सामान्य परिचय।
(ii) लोक साहित्य का भेद-उपभेद, ऐतिहासिक तथ्य, प्रकृति चित्रण, जीवन दर्शन, छंद विधान, शिल्प विम्बविधान एवं महत्व।
(iii) संथाली लोकगीतः डाहार, बाहा, काराम, दोंसाय, सोहराय, लोंगडे, डाप्ठा, रिजा, गोलवारी, बाप्ला।
(iv) लोक कथाः सृष्टि कथाएं, देव कथाएं, गोत्र कथाएं, भाई बहन की कथाएं एवं जीव-जगत कथाएं।
(v) लोक गाथा।
(vi) प्रकीर्ण साहित्यः (क) लोकोक्ति, (ख) मुहावरा, (ग) पहेली, (घ) बालगीत, (ड़) मंत्र आदि।
भाग - (ग) संथाली शिष्ट साहित्य
(i) संथाली साहित्य का काल विभाजन
1. आदिकाल-1854 ई- के पूर्व का साहित्य।
2. मध्यकाल-1854 ई- से 1946 ई- तक का साहित्य।
3. आधुनिक काल-1947 ई- से अब तक का साहित्य।
(ii) संथाली पद्य साहित्य का इतिहास एवं विकास।
(क)गीत, (ख) कविता।
(iii)संथाली गद्य साहित्य का इतिहास एवं विकास।
(क) कहानी, (ख) उपन्यास, (ग) नाटक, (घ) आत्मकथा, (ड़) जीवनी, (च) यात्र वृतान्त, (छ) निबंध, (ज) विविध संथाली साहित्य।
(iv)पद्य एवं गद्य से सप्रसंग व्याख्या।
खण्ड-II
भाग - (घ) संथाली साहित्यकार एवं साहित्य
(i) संथाली साहित्य के विकास पर अन्य भारतीय साहित्यों का प्रभाव।
(ii) संथाली साहित्य के कुछ प्रमुख कवि, लेखक, नाटककार तथा उनकी कृतियों का परिचय।
1. मांझी रामदास टुडू ‘रेसका।’
2. साधु रामचांद मुर्मू
3. पं- रघुनाथ मुर्मू
4. गोरा चांद टुडू।
5. नारायण सोरेन ‘तोड़ेसुताम’।
6. नाथनियल मुर्मू
7. डमन हांसदा।
8. ठाकुर प्रसाद मुर्मू।
9. दिगम्बर हांसदा।
10. यशोदा हांसदा मुर्मू।
11. कृष्ण चन्द्र टुडू।
भाग - (ड़) संथाली निबंध
विभिन्न विषयों पर संथाली भाषा (देवनागरी लिपि) में निबंध लेखन-
(i) समसामयिक विषय।
(ii) सांस्कृतिक विषय
(iii)सामाजिक विषय
(iv)आर्थिक विषय
(v) भौगोलिक विषय
भाग - (च) संथाली संक्षेपण
किसी एक गद्यांश का संक्षेपण।
भाग - (छ) संथाली भाषा अनुवाद
किसी एक हिन्दी गद्यांश को संथाली में अनुवाद।
भाग - (ज) संथाली अनुच्छेद
किसी एक अनुच्छेद या अवतरण पद पर संथाली भाषा में तीन प्रश्नों का उत्तर देना होगा।
झारखण्ड लोक सेवा आयोग मुख्य परीक्षा, पत्र-II
पंचपरगनिया भाषा-साहित्य
Full Marks: 150Time: 3 Hours
खण्ड-I
भाग - (क)
(i) पंचपरगनिया भाषा का उद्भव और विकास।
(ii) पंचपरगनिया भाषा की विशेषताएं।
(iii) पंचपरगनिया भाषा का व्याकरण- संज्ञा, सर्वनाम, वचन, पुरुष, लिंग, काल, क्रिया, समास, विशेषण, उपसर्ग, प्रत्यय, कारक, अव्यय।
(iv)पंचपरगनिया शब्द गठन, वाक्य संरचना एवं क्षेत्रीय रूप।
(v) देवनागरी लिपि का उद्भव, विशेषताएं तथा विकास।
(vi)पंचपरगनिया भाषा के सहोदर भाषाएं एवं संबंध।
भाग - (ख) पंचपरगनिया लोक साहित्य
(i) पंचपरगनिया लोक साहित्य का सामान्य परिचय - भेद-उपभेद, ऐतिहासिक तथ्य, प्रकृति चित्रण आदि।
(ii) पंचपरगनिया लोकगीत - जीवन दर्शन, रस छंद, अलंकार, शिल्प, विम्ब विधान, (बिहा गीत, सहरई गीत, करम गीत, पूस गीत) आदि।
(iii) पंचपरगनिया लोक कथाओं का उद्भव और विकास - सृष्टि कथाएं, देव-देवि कथाएं, गोत्र कथाएं, भाई बहन की कथाएं, पेड़-पौधे एवं जीव जन्तु आदि की कथाएं।
(iv)पंचपरगनिया लोक-गाथा
(v) पंचपरगनिया प्रकीर्ण साहित्य।
भाग - (ग) पंचपरगनिया शिष्ट साहित्य
(i) पंचपरगनिया साहित्य का काल विभाजन
1. आदिकाल, 2. मध्यकाल, 3. आधुनिक काल, 4. अत्याधुनिक काल
(ii) पंचपरगनिया पद्य साहित्य का इतिहास एवं विकास
1- गीत, 2- कविता, 3- खण्ड काव्य, 4- महाकाव्य।
(iii)पंचपरगनिया गद्य साहित्य का इतिहास एवं विकास
1. कहानी, 2. उपन्यास, 3. नाटक, 4. आत्मकथा, 5. जीवनी, 6. यात्र वृतान्त, 7. निबंध, 8. संस्मरण, 9. रेखा चित्र, 10. आलोचना।
(iv)पंचपरगनिया पद्य एवं गद्य से सप्रसंग व्याख्या
1. पद्य अंश - 10 अंक।
2. गद्य अंश - 10 अंक।
खण्ड-II
भाग - (घ) पंचपरगनिया साहित्यकार एवं साहित्य
(i) पंचपरगनिया साहित्य के विकास पर अन्य भारतीय साहित्यों का प्रभाव।
(ii) पंचपरगनिया साहित्य के प्रमुख कवि, लेखक, नाटककार के कृतियों का परिचय
बरजुराम, भवप्रीतानन्द ओझा, रामकृष्ण गांगुली, विनन्द सिंह, ज्योतिलाल महादानी, परमानन्द महतो, राज किशोर सिंह, सृष्टिधर महतो, दीनबन्धु महतो, संतोष साहु ‘प्रीतम’।
भाग - (ड़) पंचपरगनिया निबंध
निम्नलिखित विषयों में से देवनागरी लिपि में निबंध लेखन
(i) सम-सामयिक विषय
(ii) सांस्कृतिक विषय
(iii)सामाजिक विषय
(iv)पारंपरिक कलाएं
(v) आर्थिक विषय
(vi)भौगोलिक विषय
भाग - (च) पंचपरगनिया संक्षेपण
इस खण्ड में गद्यांश का शीर्षक एवं संक्षेपण करना होगा।
भाग - (छ) पंचपरगनिया भाषा अनुवाद
इस खण्ड में गद्यांश का पंचपरगनिया में अनुवाद करना होगा।
भाग - (ज) अवतरण/अनुच्छेद
इस खण्ड में दिये गये अनुच्छेद/अवतरण को पढ़ कर पंचपरगनिया भाषा में तीन प्रश्नों के उत्तर देने होंगे।
झारखण्ड लोक सेवा आयोग मुख्य परीक्षा, पत्र-II
नागपुरी भाषा-साहित्य
Full Marks: 150Time: 3 Hours
खण्ड-I
भाग - (क)
(i) नागपुरी भाषा का उद्भव और विकास
(ii) नागपुरी भाषा की विशेषताएं।
(iii) नागपुरी भाषा का व्याकरण-वर्ण, संज्ञा, सर्वनाम, वचन, पुरुष, लिंग, काल, क्रिया विशेषण, विशेषण, उपसर्ग, प्रत्यय, कारक, अव्यय।
(iv)वाक्य संरचना एवं भेद।
(v) देवनागरी लिपि का उद्भव और विकास तथा विशेषताएं।
भाग - (ख) नागपुरी लोक साहित्य
(i) नागपुरी लोक साहित्य का सामान्य परिचय।
(ii) नागपुरी लोक साहित्य के भेद-उपभेद, ऐतिहासिक तथ्य, प्रकृति चित्रण, जीवन दर्शन, राग-छंद, शिल्प-शैली, बिम्ब एवं प्रतीक विधान।
(iii) नागपुरी लोकगीत - झुमइर, मरदानी झुमइर, जनी झुमइर, बंगला झुमइर, पावस, उदासी, फगुआ, पंचरंगी पुछारी, झुमटा, लहसुआ आदि।
(iv) नागपुरी लोक कथाओं का उद्भव और विकास - सृष्टि कथाएं, पशु-पक्षी की कथाएं, भाई-बहन की कथाएं, प्रेम कथाएं, मिथ, लिजेंड एवं अन्य कथाएं।
(v) नागपुरी का प्रकीर्ण साहित्य- 1- लोकोक्ति, 2- मुहावरा, 3- बुझौवल (पहेली), 4- बालगीत, 5- खेल गीत एवं मंत्र।
भाग - (ग) नागपुरी शिष्ट साहित्य
(i) नागपुरी साहित्य का काल विभाजन
1. आदिकाल, 2. मध्यकाल, 3. आधुनिक काल
(ii) नागपुरी पद्य साहित्य का इतिहास एवं विकास।
1. गीत, 2. कविता, 3. खण्ड काव्य, 4. महाकाव्य।
(iii)नागपुरी गद्य साहित्य का इतिहास एवं विकास
1. कहानी, 2. उपन्यास, 3. नाटक, 4. आत्मकथा, 5. जीवनी, 6. यात्र वृतान्त, 7. निबंध, 8. समीक्षा (आलोचना), 9. हास्य-काव्य एवं विविध गद्य साहित्य।
(iv) पद्य एवं गद्य से सप्रसंग व्याख्या - (वन केंवरा - भाग-2 शंकुतला मिश्र एवं डॉ- उमेश नन्द तिवारी द्वारा संपादिक पुस्तक से।)
खण्ड - II
भाग - (घ) नागपुरी साहित्यकार एवं साहित्य
(i) नागपुरी साहित्य के कुछ प्रमुख कवि, लेखक, नाटककार, समीक्षक तथा उनकी कृतियों का परिचय- हनुमान सिंह, सोबरन साय, महंत घासी, घासी राम, कंचन, धनी राम बक्शी, पीटर शांति नवरंगी, योगेन्द्र नाथ तिवारी, प्रफुल्ल कुमार राय, शारदा प्रसाद शर्मा, साहनी उपेन्द्र पाल नहन, विसेश्वर प्रसाद केशरी, नईमउद्दीन मिरदाहा, लाल रण विजय नाथ शाहदेव, मधु मंसुरी हंसमुख, मुकुन्द नायक, प्रमोद कुमार राय, सी-डी- सिंह, कृष्ण प्रसाद साहू, कलाधर, गिरिधारी राम गौंझू।
(i) नागपुरी साहित्य के विकास पर अन्य भारतीय साहित्यों का प्रभाव
भाग - (ड़) नागपुरी निबंध
निम्नलिखित विषयों में से देवनागरी लिपि में निबंध लेखन
(i) सम-सामयिक विषय
(ii) सांस्कृतिक विषय
(iii)सामाजिक विषय
(iv)पारंपरिक कलाएं
(v) अखरा कला - गीत, वाद्य एवं नृत्य
(vi)झारखण्ड से संबंधित इतिहास एवं भूगोल।
भाग - (च) नागपुरी में संक्षेपण
दिये गए गद्यांश का शीर्षक एवं संक्षेपण करना होगा।
भाग - (छ) नागपुरी भाषा में अनुवाद
दिये गए गद्यांश का नागपुरी में अनुवाद करना होगा।
भाग - (ज) नागपुरी अनुच्छेद से प्रश्न
दिये गये अनुच्छेद को पढ़कर नागपुरी भाषा में दिए गए पांच प्रश्नों से तीन प्रश्नों का उत्तर देना होगा।
झारखण्ड लोक सेवा आयोग मुख्य परीक्षा, पत्र-II
मुण्डारी भाषा-साहित्य
Full Marks: 150Time: 3 Hours
खण्ड-I
भाग - (क)
(i) मुण्डारी भाषा का उद्भव और विकास।
(ii) मुण्डारी भाषा की विशेषताएं।
(iii) मुण्डारी भाषा का व्याकरण- संज्ञा, सर्वनाम, वचन, पुरुष, लिंग, काल, क्रिया, विशेषण, उपसर्ग, प्रत्यय, कारक, अव्यय।
(iv)शब्द गठन, वाक्य संरचना एवं क्षेत्रीय रूप।
(v) देवनागरी लिपि एवं मुण्डारी लिपि का उद्भव, विशेषताएं तथा विकास।
भाग - (ख) मुण्डारी लोक साहित्य
(i) मुण्डारी लोक साहित्य का सामान्य परिचय, भेद-उपभेद, ऐतिहासिक तथ्य, प्रकृति चित्रण।
(ii) मुण्डारी लोकगीत- जीवन दर्शन, रस, अलंकार, लोकगीत - जदुर, करम, विवाह गीत।
(iii) मुण्डारी लोक कथाओं का उद्भव और विकास - सृष्टि कथाएं, देव-देवी कथाएं, गोत्र कथाएं, भाई-बहन की कथाएं, पेड़-पौधे की कथाएं एवं जीव-जन्तु कथाएं आदि।
(iv) मुण्डारी प्रकीर्ण साहित्य 1. लोकोक्ति, 2. मुहावरा, 3. पहेली, 4. बालगीत, 5. खेल गीत।
भाग - (ग) मुण्डारी शिष्ट साहित्य
(i) मुण्डारी साहित्य का काल विभाजन
1. आदिकाल, 2. मध्यकाल, 3. आधुनिक काल
(ii) मुण्डारी पद्य साहित्य का इतिहास एवं विकास
1. गीत, 2. कविता
(iii)मुण्डारी गद्य साहित्य का इतिहास एवं विकास
1. कहानी, 2. उपन्यास, 3. नाटक, 4. आत्मकथा, 5. जीवनी, 6. यात्र वृतान्त, 7. निबंध, 8. विविध मुण्डारी साहित्य।
(iv)पद्य एवं गद्य से सप्रसंग व्याख्या।
खण्ड - II
भाग - (घ) मुण्डारी साहित्यकार एवं साहित्य
(i) मुण्डारी साहित्य के विकास पर अन्य भारतीय साहित्यों का प्रभाव।
(ii) मुण्डारी साहित्य के कुछ प्रमुख कवि, लेखक, नाटककार, समीक्षक तथा उनकी कृतियों का परिचय।
1. डॉ. रामदयाल मुण्डा।
2. प्रो. दुलय चन्द्र मुण्डा।
3. काण्डे मुण्डा।
4. बुदू बाबु - प्रीतपाला, रामायण पाला।
भाग - (ड़) मुण्डारी निबंध
निम्नलिखित विषयों पर मुण्डारी (देवनागरी लिपि) में निबंध लेखन
(i) सम-सामयिक विषय
(ii) सांस्कृतिक विषय
(iii)सामाजिक विषय
(iv)आर्थिक विषय
(v) भौगोलिक विषय
भाग - (च) मुण्डारी भाषा संक्षेपण
किसी एक गद्यांश का संक्षेपण।
भाग - (छ) मुण्डारी भाषा अनुवाद
किसी एक हिन्दी गद्यांश का मुण्डारी में अनुवाद।
भाग - (ज) मुण्डारी अनुच्छेद से प्रश्न
किसी एक अनुच्छेद या अवतरण पढ़कर मुण्डारी भाषा में तीन प्रश्नों का उत्तर देना होगा।
झारखण्ड लोक सेवा आयोग मुख्य परीक्षा, पत्र-II
कुंडुख भाषा-साहित्य
Full Marks: 150Time: 3 Hours
खण्ड-I
भाग - (क)
(i) कुंडुख भाषा का उद्भव और विकास।
(ii) कुंडुख भाषा की विशेषताएं
(iii) कुंडुख भाषा का व्याकरण- संज्ञा, सर्वनाम, वचन, पुरुष, लिंग, काल, क्रिया, विशेषण, उपसर्ग एवं प्रत्यय, कारक, जीव, अव्यय
(iv)शब्द गठन, वाक्य संरचना एवं क्षेत्रीय रूप।
(v) देवनागरी लिपि एवं तोलोंगसिकी लिपि का उद्भव, विकास, विशेषताएं।
(vi)कुंडुख भाषा की सहोदर भाषाएं एवं संबंध।
भाग - (ख) कुंडुख लोक साहित्य
(i) कुंडुख लोक साहित्य का सामान्य परिचय।
(ii) लोक साहित्य का भेद-उपभेद, ऐतिहासिक तथ्य, प्रकृति चित्रण आदि जीवन दर्शन, छंद
(iii) कुंडुख लोकगीत - खद्दी, राजी करम, घुडिया करम, जेठ जतरा, कार्तिक जतरा, जदुरा, असारी, सवनिया, माठा, बरोया, बैंजा आदि तथा आधुनिक कविताएं।
(iv) लोक कथा - सृष्टि कथाएं - डण्डा कट्टना की कथा, गोत्र कथाएं, भाई-बहन की कथाएं एवं जीव-जगत की कथाएं।
(v) प्रकीर्ण साहित्य – 1. लोकोक्ति, 2. मुहावरा, 3. पहेली, 4. बालगीत, 5. मंत्र आदि।
भाग - (ग) कुंडुख शिष्ट साहित्य
(i) कुंडुख साहित्य का काल विभाजन
1. आदिकाल - 1868-1900
2. मध्यकाल - 1901-1951
3. आधुनिक काल - 1952 - अबतक
(ii) कुंडुख पद्य साहित्य का इतिहास एवं विकास-
1. गीत
2. कविता
(iii)कुंडुख गद्य साहित्य का इतिहास एवं विकास-
कहानी, नाटक, उपन्यास, आत्मकथा, जीवनी, यात्र वृतान्त, निबंध एवं विविध कुंडुख साहित्य।
(iv)गद्य एवं पद्य से सप्रसंग व्याख्या।
खण्ड-II
भाग - (घ) कुंडुख साहित्यकार एवं साहित्य
(i) कुंडुख साहित्य के विकास पर अन्य भारतीय साहित्य का प्रभाव।
(ii) कुंडुख साहित्य के कुछ प्रमुख कवि, लेखक, नाटककार तथा उनकी कृतियों का परिचय-
1. दवले कुजूर
2. इग्नेस कुजूर
3. अहलाद तिर्की
4. बिहारी लकड़ा
5. पी-सी- बेक
6. डॉ. निर्मल मिंज
7. अलबिनुस मिंज
8. शांति प्रकाश प्रबल बाखला
9. इंद्रजीत उरांव
10 भिखराम भगत
भाग - (ड़) कुंडुख निबंध
विभिन्न विषयों पर कुंडुख भाषा (देवनागरी लिपि) में निबंध लेखन
1. सम-सामयिक विषय
2. सांस्कृतिक विषय
3. सामाजिक विषय
4. आर्थिक विषय
5. भौगोलिक विषय
6. राजनैतिक विषय
भाग - (च) कुंडुख संक्षेपण
1. किसी एक गद्यांश का संक्षेपण
भाग - (छ) कुंडुख भाषा अनुवाद
किसी एक हिन्दी गद्यांश को कुंडुख में अनुवाद
भाग - (ज) कुंडुख अनुच्छेद
किसी एक अनुच्छेद या अवतरण पढ़कर कुंडुख भाषा में तीन प्रश्नों का उत्तर देना होगा।
झारखण्ड लोक सेवा आयोग मुख्य परीक्षा, पत्र-II
कुरमाली भाषा-साहित्य
Full Marks: 150Time: 3 Hours
खण्ड-I
भाग - (क)
(i) कुरमाली भाषा का उद्भव और विकास
(ii) कुरमाली भाषा की प्रकृति एवं विशेषताएं।
(iii)कुरमाली भाषा की स्थानीय विभिन्नताएं।
(iv)देवनागरी लिपि का उद्भव, विशेषताएं तथा विकास।
(v) कुरमाली भाषा का व्याकरण एवं वाक्य संरचना।
भाग - (ख) कुरमाली लोक साहित्य
(i) कुरमाली लोकसाहित्य: कुरमाली के लोकगीत, मुहावरे, लोकोक्तियां, पहेलियां।
(ii) कुरमाली लोककथा: वर्गीकरण एवं महत्व।
(iii)कुरमाली लोकनाट्य
भाग - (ग) कुरमाली शिष्ट साहित्य
(i) कुरमाली साहित्य का काल-विभाजन विशेषताएं एवं प्रवृत्तियां
1. आदिकाल, 2. मध्यकाल, 3. आधुनिक काल
(ii) कुरमाली पद्य साहित्य का विकास: कालक्रमानुसार काव्य की विशेषताएं, आधुनिक गीत, आधुनिक काव्य/कविता की प्रवृत्तियां।
(iii)कुरमाली गद्य साहित्य का विकास
1. कहानी, 2. उपन्यास, 3. नाटक, 4. निबंध, 5. संस्मरण एवं 6. आलोचना।
(iv)सप्रसंग व्याख्या
1. पद्य भाग
2. गद्य भाग
खण्ड - II
भाग - (घ) कुरमाली साहित्य एवं साहित्यकार
(i) कुरमाली साहित्य के प्रमुख कवि, लेखक, नाटककार की कृतियों का परिचय: डॉ- नन्द किशोर सिंह, बसंत कुमार मेहता, लखीकान्त मुतरुदार, केशव चन्द्र महतो, कालिपदो महतो, खुदि राम महतो, सुरेन्द्र नाथ महतो, अनन्त महतो, डॉ- मानसिंह महतो, डॉ- हरदेव नारायण सिंह।
(ii) कुरमाली साहित्य के विकास पर अन्य साहित्यों का प्रभाव।
भाग - (ड़) कुरमाली निबंध लेखण
निम्नलिखित विषयों पर कुरमाली भाषा (देवनागरी लिपि) में निबंध लेखन
(i) सम-सामयिक विषय
(ii) सांस्कृतिक विषय
(iii)सामाजिक विषय
(iv)आर्थिक
भाग - (च) कुरमाली भाषा संक्षेपण
संक्षेपण।
भाग - (छ) कुरमाली भाषा अनुवाद
अनुवाद: हिन्दी से कुरमाली में या कुरमाली से हिन्दी में।
भाग - (ज) कुरमाली अनुच्छेद से प्रश्न
अलक्षित अवतरण से प्रश्न।
झारखण्ड लोक सेवा आयोग मुख्य परीक्षा, पत्र-II
खोरठा भाषा-साहित्य
Full Marks: 150Time: 3 Hours
खण्ड-I
भाग - (क) खोरठा भाषा
(i) खोरठा भाषा का उद्भव और विकास।
(ii) खोरठा भाषा की विशेषताएं।
(iii) खोरठा भाषा का व्याकरण- संज्ञा, सर्वनाम, वचन, पुरुष, लिंग-निर्णय, काल, क्रिया, विशेषण, उपसर्ग, प्रत्यय, कारक।
(iv)शब्द गठन एवं वाक्य संरचना एवं क्षेत्रीय रूप, मानकीकरण।
(v) लिपि समस्या, विशेषताएं तथा विकास।
(vi)खोरठा भाषा का झारखण्ड की अन्य भाषाओं से संबंध एवं विभिन्नता।
भाग - (ख) खोरठा लोक साहित्य
(i) खोरठा लोक साहित्य का सामान्य परिचय, विशेषताएं एवं महत्व।
(ii) खोरठा लोकगीत की परिभाषा, विशेषताएं एवं महत्व, खोरठा लोकगीतों का वर्गीकरण, लोकगीतों में विविध-चित्रण।
(iii)खोरठा लोक कथाओं का उद्भव और विकास, वर्गीकरण एवं महत्व।
(iv)लोकगाथा।
(v) खोरठा प्रकीर्ण साहित्य- (क) लोकोक्ति, (ख) मुहावरा, (ग) पहेली, (घ) मंत्र।
भाग - (ग) खोरठा शिष्ट साहित्य
(i) खोरठा साहित्य का काल विभाजन-
1. आदिकाल, 2. मध्यकाल, 3. आधुनिक काल
(ii) खोरठा पद्य साहित्य का उद्भव एवं विकास।
1. गीत, 2. कविता।
(iii)खोरठा गद्य साहित्य का इतिहास एवं विकास-
1. कहानी, 2. उपन्यास, 3. नाटक, 4. आत्मकथा, 5. जीवनी, 6. यात्र वृतान्त, 7. निबंध, 8. शब्द चित्र, 9. संस्मरण।
खण्ड-II
भाग - (घ) खोरठा साहित्यकार एवं साहित्य
(i) खोरठा साहित्य के विकास पर अन्य भारतीय साहित्यों का प्रभाव।
(ii) खोरठा भाषा साहित्य के प्रमुख कवि, लेखकों, कालाकारों की कृतियों का परिचय - श्री निवास पानुरी, भुवनेश्वर दत्त शर्मा व्याकुल, ए-के- झा, श्याम सुन्दर महतो, विश्वनाथ दसौधी राज, विश्वनाथ नागर, शिवनाथ प्रमाणिक, कुमारी शशि, डॉ- विनोद कुमार, डॉ- वी-एन- ओहदार।
भाग - (ड़) खोरठा निबंध
निम्नलिखित विषयों में से देवनागरी लिपि में निबंध लेखन
(i) सम-सामयिक विषय पर निबंध
(ii) सांस्कृतिक विषय
(iii)सामाजिक विषय
(iv)आर्थिक विषय
(v) भौगोलिक विषय
भाग - (च) खोरठा संक्षेपण
दिये गए गद्यांश का शीर्षक एवं संक्षेपण करना होगा।
भाग - (छ) खोरठा गद्यांश
इस भाग में परीक्षार्थियों को दिए गए हिन्दी गद्यांश को खोरठा भाषा (देवनागरी लिपि) में अनुवाद।
भाग - (ज) खोरठा अनुच्छेद से प्रश्न
इस भाग में परीक्षार्थियों को दिए गए अनुच्छेद/अवतरण पढ़कर खोरठा भाषा में तीन प्रश्नों का उत्तर देना है।
झारखण्ड लोक सेवा आयोग मुख्य परीक्षा, पत्र-II
खडि़या भाषा-साहित्य
Full Marks: 150Time: 3 Hours
खण्ड-I
भाग - (क) खडि़या भाषा
(i) खडि़या भाषा का उद्भव और विकास।
(ii) खडि़या भाषा की विशेषताएं।
(iii) खडि़या भाषा का व्याकरण- संज्ञा, सर्वनाम, वचन, पुरूष, लिंग, काल, क्रिया, विशेषण, उपसर्ग, प्रत्यय, कारक, अव्यय।
(iv)शब्द गठन, वाक्य संरचना एवं क्षेत्रीय रूप।
(v) देवनागरी लिपि एवं खडि़या लिपि का उद्भव, विशेषताएं एवं विकास।
(vi)खडि़या भाषा के सहोदर भाषाएं एवं संबंध।
भाग - (ख) खडि़या लोक साहित्य
(i) खडि़या लोक साहित्य का सामान्य परिचय, भेद-उपभेद, ऐतिहासिक तथ्य, प्रकृति चित्रण।
(ii) खडि़या लोकगीत - जीवन दर्शन, रस, अलंकार।
लोकगीत-जड़कोर, बन्दोई, करम परब, जनम परब।
(iii) खडि़या लोक कथाओं का उद्भव और विकास- सृष्टि कथाएं, पशु-पक्षी की कथाएं, मूर्ख-कथाएं, गोत्र-कथाएं, भाई-बहन की कथाएं।
(iv)लोकगाथा।
(v) खडि़या प्रकीर्ण साहित्य – 1. लोकोक्ति, 2. मुहावरे, 3. पहेली, 4. बालगीत, 5. खेल गीत, 6. मंत्र।
भाग - (ग) खडि़या शिष्ट साहित्य
(i) खडि़या साहित्य का काल विभाजन
1. आदिकाल - आरंभ से 1934 ई- तक
2. मध्यकाल - 1935 से 1979 तक
3. आधुनिक काल - 1979 से आज तक।
(ii) खडि़या पद्य साहित्य का इतिहास एवं विकास।
1. कविता, 2. गीत।
(iii)खडि़या गद्य साहित्य का इतिहास एवं विकास-
1- कहानी, 2- उपन्यास, 3- नाटक, 4- आत्मकथा, 5- जीवनी, 6- यात्र वृतान्त, 7- निबंध, 8- विविध खडि़या साहित्य।
(iv)पद्य एवं गद्य से सप्रसंग व्याख्या।
खण्ड - II
भाग - (घ) खडि़या साहित्यकार एवं साहित्य
(i) खडि़या साहित्य के विकास पर अन्य भारतीय साहित्यों का प्रभाव।
(ii) खडि़या साहित्य के कुछ प्रमुख कवि, लेखक, नाटककार तथा उनकी कृतियों का परिचय।
1. खीस्त प्यारा केरकेट्टा
2. जुलियुस बा
3. डॉ. रोज केरकेट्टा
4. डॉ. आर-पी- साहू
5. फा. पौलुस कुल्लू
6. सैमुएल बागे
7. डॉ. इग्नासिया टोप्पो
8. फा. जोवाकिम डुंगडुंग
9. नुअस केरकेट्टा
10. मेरी एस- सोरेंग
भाग - (ड़) खडि़या निबंध
विभिन्न विषयों पर खडि़या भाषा देवनागरी लिपि में निबंध लेखन
(i) सम-सामयिक विषय
(ii) सांस्कृतिक विषय
(iii)सामाजिक विषय
(iv)आर्थिक विषय
(v) भौगोलिक विषय
भाग - (च) खडि़या संक्षेपण
किसी एक गद्यांश का संक्षेपण।
भाग - (छ) खडि़या भाषा अनुवाद
किसी एक हिन्दी गद्यांश का खडि़या भाषा में अनुवाद।
भाग - (ज) खडि़या अनुच्छेद से प्रश्न
किसी एक अनुच्छेद या अवतरण पढ़कर खडि़या भाषा में तीन प्रश्नों का उत्तर देना होगा।
झारखण्ड लोक सेवा आयोग मुख्य परीक्षा, पत्र-II
हो भाषा-साहित्य
Full Marks: 150Time: 3 Hours
खण्ड-I
भाग - (क)
(i) हो भाषा का उद्भव और विकास।
(ii) हो भाषा की विशेषताएं।
(iii) हो भाषा का व्याकरण- संज्ञा, सर्वनाम, वचन, पुरूष, लिंग, काल, क्रिया, विशेषण, उपसर्ग, प्रत्यय, कारक अनेक शब्दों के बदले एक शब्द, पर्यायवाची शब्द।
(iv)शब्द गठन एवं वाक्य संरचना एवं क्षेत्रीय रूप।
(v) देवनागरी लिपि एवं वारड, चिति लिपि का उद्भव, विकास एवं विशेषताएं।
(vi)हो भाषा के सहोदर भाषाएं एवं संबंध।
भाग - (ख) हो लोक साहित्य
(i) हो लोक साहित्य का सामान्य परिचय, भेद-उपभेद, ऐतिहासिक तथ्य, प्रकृति चित्रण।
(ii) हो लोकगीत - जीवन दर्शन, रस, अलंकार। लोकगीत: बा, मागे, हेरो, जोमनमा अणादि।
(iii) लोक कथाओं का उद्भव और विकास- सृष्टि कथाएं, पशु-पक्षी की कथाएं, मूर्ख-कथाएं, गोत्र-कथाएं, भाई-बहन की कथाएं।
(iv)लोकगाथा।
(v) हो प्रकीर्ण साहित्य – 2. लोकोक्ति, 2. मुहावरा, 3. पहेली, 4. बालगीत, 5. मंत्र।
भाग - (ग) हो शिष्ट साहित्य
(i) हो साहित्य का काल विभाजन
1. आदिकाल
2. मध्यकाल
3. आधुनिक काल
(ii) हो पद्य साहित्य का इतिहास एवं विकास-
1. कविता
2. गीत
(iii)हो गद्य साहित्य का इतिहास एवं विकास-
1. कहानी, 2. उपन्यास, 3. नाटक, 4. आत्मकथा, 5. जीवनी, 6. यात्र वृतान्त, 7. निबंध, 8. विविध हो साहित्य।
(iv)पद्य एवं गद्य से सप्रसंग व्याख्या।
खण्ड - II
भाग - (घ) हो साहित्यकार एवं साहित्य
(i) हो साहित्य के विकास पर अन्य भारतीय साहित्यों का प्रभाव।
(ii) हो साहित्य के कुछ प्रमुख कवि, लेखक, नाटककार, समीक्षक तथा उनकी कृतियों का परिचय।
1. लको बोदरा।
2. बलराम पाट पिगुआ
3. कमल लोचन कोडाह
4. डॉ- आदित्य प्रसाद सिन्हा
5. धनुर सिंह पुरती
6. दुर्गा पुरती
7. विश्वनाथ बोदरा
8. कान्हूराम देवगम
9. सतीश कुमार कोडाह
10. शंकर लाल गागराई
11. कृष्ण कुंकल
12. हरिहर सिंह सिरका।
भाग - (ड़) हो निबंध
निम्नलिखित विषयों में से देवनागरी लिपि में निबंध लेखन
(i) सम-सामयिक
(ii) सांस्कृतिक
(iii)सामाजिक
(iv)आर्थिक
(v) साहित्यिक
(vi)धार्मिक
(vii)शहीद से संबंधित
(viii)ऐतिहासिक
भाग - (च) हो संक्षेपण
किसी एक गद्यांश का संक्षेपण।
भाग - (छ) हो भाषा अनुवाद
किसी एक हिन्दी गद्यांश को हो में अनुवाद।
भाग - (ज) हो अनुच्छेद से प्रश्न
किसी एक अनुच्छेद या अवतरण पढ़कर हो भाषा में तीन प्रश्नों का उत्तर देना होगा।
Paper-III
social Sciences (History and Geography)
Full Marks: 200Time: 3 Hours
The question paper of social sciences shall have two distinct sections: one of history and the other one of Geography; each of 100 marks. The candidates will be required to answer one compulsory and two optional questions from each section i.e. six question in all. The compulsory question of each section, covering the entire syllabus of the concerned section, shall have ten objective type questions each of two marks (10 × 2 = 20 marks). In addition, there shall be four optional questions in each section of History and Geography. Since there are four distinct sub-sections, both in History and Geography, one question will be drawn from each sub-section as to make a total of four optional questions in each of the two distinct sections of History and Geography, of which candidates will be required to answer only two questions; each of 40 marks. The optional questions shall be answered in the traditional, descriptive style, requiring long answers.
Section (A) – History : 100 Marks
(A)Ancient Period
(i)The Indus Valley Civilization origin, antiquity, extent, authorship and main features.
(ii)Origin of the Aryans
(iii)Antiquity and stratification of the Vedic literature, Society, economy and religion during early (Rig-Vedic) period.
(iv)The Lichchhavis and their republican constitution
(v)The Rise of the Magadha empire.
(vi)The Mauryas : Extent of empire, Kalinga war and its impact; Asoka's Dhamma, Foreign policy, development of Art and Architecture during the Mauryan period
(vii) The Kushanas : Kanishka: Extent of empire his religious policy. Development of Art, Architecture and letters during the Kushana period.
(viii)The Guptas: Extent of empire development of language and literature art and architecture during the Gupta period.
(ix)Harshvardhan: The last great Hindu ruler of Northern India cultural achievements during his period.
(x)The Cholas: Maritime activities in south-east Asian countries Chola administration, art and architecture.
(xi)Cultural achievements of the Pallavas.
(B)Medieval Period:
(xii) The Arab Invasion of India.
(xiii)The Ghaznavid invasion of India
(xiv)The Delhi Sultanate : Market and Military reforms of Allauddin Khilji utoplan policies of Muhammad -bin-Tuglaq
(xv) The Mongol invasion of India.
(xvi) Religious movements: (a) Sufism, (b) Bhakti Movement
(xvii) Dawn of a New Islamic culture: Indo-Islamicarchitecture development of Urdu and Hindi languages.
(xviii) The Mughals: First Battle of Panipat: Achievements of Sher Shah Suri, Consolidation of Mughal empire. Establishment of Jagirdari and Mansabdari systems under Akbar. Akbar’s religious and Rajput policies, Aurangzeb’s religious and Rajput policies, Mughal architecture and painting, economic condition during Mughal period.
(xix) The rise of the Marathas: Achievements of Shivaji, Northward expansion of the Marathas and their downfall.
(C)Modern Period:
(xx)Beginning of European settlements: Formation and growth of East India Company consolidation of British power in India. battles of Plassey and Buxar. Control over Mysore Subsidiary Alliance, doctrine of Lapse, Doctrine of Escheat.
(xxi)Resistance to colonial rule: Peasant, Tribal and cultural Renaissance, revolt of 1857.
(xxii)Social reforms movements in Hindu community: Brahma Samaj, Arya Samaj, RamKrishna Mission, Prarthana Samaj and Theosophical society of India.
(xxiii)Social Reforms Movements in Muslim Community : Wahabi Movement and Alligarh Movement.
(xxiv)Struggle for Raising Women’s status: Abolition of Sati system, Widow Marriage Act, Consent Bill, Stress on Female Education.
(xxv)Land Revenue Administration under the British rule Permanent Settlement Ryotwari and Mahalwari Systems.
(xxvi)Rise of Nationalism in India in the 19th century: Formation of Indian National Congress: Moderates and Extremists Swadeshi Movement, Home Rule League Movement, Khillafat Movement.
(xxvii) Mahatma Gandhi and Mass Politics: Non Co-operation Movement, Civil Disobedience Movement, Quit India Movement.
(xxviii) The partition of India and its consequences.
(xxix)India after Independence: Integration of princely states in Indian Union, Linguistic Reorganization of States; Non-aligned policy under Nehru and Indra Gandhi, Libration of Bangladesh.
(D)History of Jharkhand:
(xxx)Adi-dharma i.e. Sarana cult of Jharkhand tribals;
(xxxi)Concept of Sadan and emergence of Nagpuria language;
(xxxii)Tribal Revolts in Jharkhand and Nationalist struggle;
(xxxiii) Birsa Movement;
(xxxiv) Tana Bhagat Movement and
(xxxv)Freedom Movement in Jharkhand
Section (B) - Geography : 100 Marks
(A)Physical Geography (General Principles)
(i)Origin and evolution of earth, interior of earth, Wegner's Continental Drift Theory; plate tectonics, volcanoes, Earthquakes and Tsunamis.
(ii)Major types of rocks and their characteristics, evolution and characteristics of landforms in the Fluvial, Glacial Arid and Karst regions.
(iii)Geomorphic processes: Weathering mass, wasting erosion and deposition, soil formation, Landscape cycles, ideas of Davis and Penck.
(iv)Composition Structure and Stratification of the atmosphere.
(v)Insolation, heat budget of the earth.
(vi)Horizontal and vertical distribution of temperature, inversion of temperature.
(vii)Air masses and fronts, Tropical and temperate cyclones.
(viii)Evaporation and condensation dew, frost, fog, mist and cloud, rainfall types.
(ix)Classification of climates (Koppen and Thornthwalte) Greenhouse effect, global warming and climate change.
(x)Hydrological cycle, distribution of temperature and solicits in the oceans and seas, waves, tides and currents, ocean floor relief features.
(B)Physical and Human Geography of India:
(xi)Structure, relief and physiographic divisions, Drainage Systems: Himalayan and the Peninsular.
(xii)Indian monsoon, mechanism onset and retreat, climatic types (Koppen and Trewartha) Green Revolution and its impact on major crops of India, Food scarcity.
(xiii)Natural Vegetation-Forest types and distribution, wild life, conservation, biosphere reserves.
(xiv)Major types of soils, (ICAR Classification) and their distribution, soil degradation and conservation.
(xv)Natural Hazards: Floods, Droughts, cyclones, Landslides.
(xvi)Population growth, distribution and density.
(xvii)Age: Sex ratio, rural-urban composition
(xviii)Population, environment and development.
(xix)Types of settlements: rural and urban, urban morphology, functional classification of urban settlements, problems of human settlement in India.
(C)Natural Resources of India: Development and Utilization
(xx)Land Resources : General land use, agricultural land use, geographical condition and distribution of major crops like Rice, Wheat, Cotton, Jute, Sugarcane, Rubber, Tea and Coffee.
(xxi)Water Resources: Availability and utilization for Industrial and other purposes, irrigation, scarcity of water, methods of conservation-rain water harvesting and watershed management, ground water management.
(xxii)Minerals and Energy Resources: Distribution and utility of (a) metallic minerals (Ion ore, copper, bauxite, Maganese), (b) non-metallic and conventional minerals (coal,
petroleum and natural gas). (c) hydro electricity and non conventional sources of
energy (solar, Wind, bio-gas). (d) energy sources, their distribution and conservation.
(xxiii)Development of Industries: Types of Industries, factors of industrial location, distribution and changing pattern of selected industries (Iron and steel, cotton textile, sugar and petrochemicals): Weber's theory of industrial location its relevance in the modern world.
(xxiv)Transport, Communication and International Trade :
(a) Roads, railways and water ways.
(b) Bases of International trade, changing pattern of India's foreign trade.
(D)Geography of Jharkhand and Utilization of its Resources
(xxv)Geological history: Landforms, drainage, climate, soil types and forests agriculture and irrigation, Damodar & Suberna rekha valley projects; mineral resources of Jharkhand, their extraction and utilization.
(xxvi)Population: Growth, distribution, density, Tribal population and their distribution, problems of tribes and Tribal development, plans; their customs, rituals festivals etc.
(xxvii)Industrial and urban development, Major Industries: Iron, Steel and Cement, Cottage Industries.
(xxviii) Pattern of urban settlement and Pollution Problems.
Paper-IV
indian constitution & polity, public administration
& good governance
Full Marks: 200Time: 3 Hours
The question-paper of the Indian Constitution Polity and Public Administration shall consist of two distinct sections i.e. one on Indian Constitution and Polity and the other one on Public Administration and Good Governance, each of 100 marks. The candidates will be required to answer one compulsory and two optional questions from each section. The compulsory question of each section, covering the entire syllabus of the concerned section, shall have ten objective type of questions, each of two marks (10×2 = 20). In addition, there shall be four optional questions in each section of which candidates will be required to answer only two questions, each of 10 marks. The optional questions shall be answered in the traditional descriptive form; requiring long answers.
Section (A) - Indian Constitution and Polity
(i)Preamble of the Indian Constitution (secular, Democratic and Socialist)-Philosophy behind it.
(ii)Salient features of the Indian Constitution, concept of public interest, litigation; Basic structure of the Indian Constitution.
(iii)Fundamental Rights and Duties.
(iv)Directive Principles of the State Policy.
(v)Union Government:
(a)Union Executive: Powers and functions of President, vice President, Prime Minister and the Council of Ministers, Functioning under a coalition Government.
(b)Union legislature: Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha : Organization and Functions; Law making process; Parliamentary Committees ; Parliament's control over Executive; Privileges and Immunities of parliament and its Members.
(c)Union Judiciary: The Supreme Court : Its role and powers principles of Natural Justice & Rule of Law, Judicial Review and Judicial Activism;
(vi)State Government:
(a)State Executive: Powers and functions of Governor, Chief Minister and the Council of Ministers.
(b)State Legislature: Organization, Powers and functions, with special reference to Jharkhand.
(c)State Judiciary: High Court: Organization, powers and functions, subordinate Judiciary.
(d)The Panchayats and the Municipalities: Constitution, powers, functions and responsibilities with special reference to 73rd and 74th constitutional amendments.
(vii)Centre-State Relationship: Administrative, Legislative and Financial.
(viii)Provisions relating to Administration of scheduled Areas and scheduled Tribal Areas.
(ix)Special provisions relating to reservation of seats for S.C. and S.T. in Legislature Services etc.
(x)Emergency provisions of the constitution.
(xi)Comptroller and Auditor-General of India (CAG)
(xii)Election Commission of India.
(xiii) Political Parties and Pressure Groups.
Section (B) - Public Administration and Good Governance
(xiv) Public Administration : Introduction, meaning, scope and significance.
(xv) Public and Private Administration.
(xvi) Union Administration: Central Secretariat, Cabinet Secretariat, Prime Minister's Office, Planning Commission, Finance Commission.
(xvii) State Administration: State Secretariat, Chief Secretary, Chief Minister's Office.
(xviii) District Administration : Origin and development of the office of the district Magistrate and Collector; changing Role of the District Collector, Impact of the separation of Judiciary on District Administration.
(xix) Personal Administration: Recruitment of Civil Services: Union Public Service Commission and the State Public Service Commission, Training of Civil Servants; Leadership and its qualities; Employee's morale and productivity.
(xx) Delegation, Centralization and de-centralization of authority.
(xxi) Bureaucracy: Origin; Its merits and demerits, Role of Bureaucracy in Policy formulation and its Implementation. Nexus between Bureaucracy and political Executive; Generalist versus specialist.
(xxii) Development Administration.
(xxiii) Disaster Management: Causes Meaning and Classification of Disaster, Disaster Mitigation: Immediate and Long-term measures.
(xxiv) Good Governance: Meaning and concept of Good and Responsive Governance; Main features of Good Governance : Accountability, Transparency, Honesty and Quick Delivery. Role of Civil Society and Peoples, participation in Good Governance, Grievance Redressal Machanism: Lokpal, Lokayukta, Central Vigilance Commissioner citizen's charter: Object Machinery and Measures provided in (i) Right to Service Act, (ii) Right to Information Act, (iii) Right to Education Act, (iv) The Consumer Protection Act, (v) Domestic Violence against women (prevention) Act, (vi) Old Age Act.
(xxv) Human Rights: Concept and meaning, universal declaration of human rights, National Human Rights Commission, State Human Rights Commission, Human Rights and Social Issues, Human Rights and Terrorism.
paper-v
indian economy, globalization and sustainable development
total Marks : 200Time: 3 hours
The question-paper on Indian Economy Globalization and Sustainable Development shall consist of five sections. Section I shall be compulsory. This section shall contain 20 objective questions each of two marks (20 × 2 = 40 marks). The 20 objective questions of this section shall be drawn from the entire syllabus of the paper of which 6 questions will be drawn from Group A and from Group B, 4 from Group C and 4 from Group D of the syllabus. Section II, III, IV and V of the question paper shall have two optional questions each drawn respectively from Groups A, B, C and D of the syllabus of which the candidates will be required to answer one question from each group, each question carrying 40 marks. Thus altogether the candidates will be required to answer one objective type compulsory question carrying 40 marks and 4 optional questions, each carrying 40 marks. The optional questions shall be answered in the traditional descriptive form; requiring long answers.
Group (A) - Basic Features of Indian Economy
(i)National Income: Elementary concepts of national income and methods of its calculation e.g. GDP, GNP, NDP, NNP, GSDP, NSDP, DDP at constant and current prices at factor cost etc.
(ii)Inflation: Concept, control of inflation: monetary, fiscal and direct measures.
(iii)Demographic features: Work force composition, demographic dividend with special reference to census of 2011: National Population Policy.
(iv)Agriculture and Rural Economy: Importance of agriculture in national economy; agricultural growth in India-production & productivity, causes of low productivity and measures taken by government in improve agricultural production. Green Revolution, Ever Green Revolution and Rainbow revolution; WTO and agriculture, Marketing and pricing of agricultural inputs and outputs.
(v)Industrial Economy : Policy initiative and charges.
(vi)Public Finance: nature, importance and scope of public finance, public Revenue Principles and types of taxation; direct, indirect progressive and proportional concept of VAT.
(vii) Public Expenditure: Theories of public expenditure, causes of growth of public expenditure and its impact on economy, internal and external borrowings.
(viii) Budget: Principles of budgeting, types of budgeting, performance based, zero based FRMD
(ix)Fiscal policy: Concept and role of fiscal policy in achieving employment, stability and economic development.
(x)Centre State fiscal relationship, role of finance Commission; Financial aspects of 73rd and 74th constitutional amendments.
(xi)Structure of Indian monetary and banking system in India.
(xii) (A) Composition and direction of India's trade: Balance of payment problem.
Group (B) - Sustainable Development, Economic Issues and Indian Development Strategy
(xii) Meaning and Measurement of Economic Development, Characteristics of Under Development.
(xiii) Indicators of development HDI, GDI, GEM: India's HDI progress
(xiv) Role of Foreign capital and technology in growth of economy.
(xv) Sustainable development: concept and indicators of sustainable development economic social and environmental sustainability, concept of Green GDP, Strategy and policy for sustainable development in India.
(xvi)Meaning of inclusive growth and development policy and strategy during 11th and 12thFive Year Plans.
(xvii) Development status and issues pertaining to socially and economically marginalised sections, like STs, SCs, religious minorities, backward castes and women, schemes launched for their development by Central/State Governments including TSP, SCSP and minorities.
(xviii) Poverty and un-employment: Measurements and trends; identification of BPL families HPI, Multi Dimensional Indian Poverty Index.
(xix) Food and Nutritional Security: Trends in food production and consumption in India. Problem of Food Security: Problems and issues of storage, procurement distribution, import and export, Government policies schemes and programmes such as PDS, ICDS and Mid-day Meal etc.
(xx) Governmental policies for food and nutritional security.
(xxi) Planning Strategy: Objectives and strategy of Indian Five Year Plans Functions and Role of NDC. Planning Commission.
(xxii) Decentralized Planning: Meaning and importance, PRIS and decentralised planning, major initiatives in India.
Group (C) - Economic Reforms, Nature and impact on Indian Economy
(xxiii)New economic reforms, Liberalization, Privatization and Globalization, rationale and need for reforms International financial institutions IMP, World Bank, WTO, their role and impact on Indian economy.
(xxiv) Financial and Banking sector reforms, economic reforms and rural banking impact on rural credit: sources and problems of rural credit institutional credit, SHG, micro finance, NABARD, RRBs, scheduled Commercial Banks, rural co-operatives financial inclusion.
(xxv) Globalization of Indian economy: Its positive and negative impacts on different sectors, issues of FDI and FH in India.
(xxvi) Agricultural sector reforms and its impact on growth, issues of subsidies and public investment on agriculture reforms and agrarian crisis.
(xxvii) Industrial development and Economic reforms in India: Major changes in industrial policy. Its impact on industrial growth and problems of SMEs; role of Public Sector enterprises in India's industrialization in post reforms period, Disinvestment and Privatisation of Public Enterprises.
Group (D) - Economy of Jharkhand: Features, Issues, Challenges and Strategies
(xxviii) Economic growth and structure of Jharkhand's economy, sectoral composition, growth in SDP and per capita NSDP in last decade Agricultural and Industrial growth in Jharkhand.
(xxix) Demographic features of Jharkhand: Population growth, sex ratio, density, literacy, composition of work force, rural-urban composition etc with special reference to Census of 2001 and 2011, inter district variations.
(xxx) Status of poverty, unemployment, food security, malnutrition, education and health indicators in Jharkhand, major initiatives, issues of agricultural and rural development, major programs and schemes; poverty alleviation programs; PURA, Bharat Nirman, MGNREGA, PMGSY, SGSY, IAY, NRLM etc., Food security schemes.
(xxxi) Land, forest and environmental issues in Jharkhand: Land reforms and agrarian relations, tribal land alienation, development induced displacement people; its impacts and policy initiatives. Forest issues and implementation of FRA, Environmental degradation and State policy to deal with to.
(xxxii) Five year plans in Jharkhand strategy and achievement in X and XIth plan, TSP and SCSP, public finance trends in Jharkhand, industrial, policy in Jharkhand and industrial development.
Paper-VI
general science environment and technology development
Total Marks: 200Time: 3 Hours
The question paper of General Science, Environment and Technology Development shall have six sections Section-I, shall have 20 objective type of questions each of 2 marks (20 × 2 = 40 marks). Questions for this section will be drawn at the rate of four questions from each of the five Groups of the syllabus Sections II, III, IV, V and VI of the question paper shall have two optional questions each drawn respectively from Groups A, B, C, D and E of the syllabus; of which candidates will be required to answer only one question from each group, each question carrying 32 marks. Optional questions shall be answered in the traditional manner, requiring descriptive answers not exceeding 500 to 600 words. Thus, altogether candidates will be required to answer one objective type compulsory question (40 marks) and five descriptive type optional question (5 × 32 = 160 marks).
Group (A) Physical Science
(i)Systom of Units: MKS, CGS and SI,
(ii)Definition of speed, velocity, gravity, mass, weight, force, impact, work, power and energy.
(iii)Solar system, relative position of Earth with respect to Sun and other planets, movement of earth and moon in solar system, lunar and solar eclipses.
(iv)Concept and nature of sound, Wave length and frequency, infrasonic and Ultrasonic sounds, sources of Infrasonic sound in nature, ultrasonic sound characteristics and some applications.
Group (B) Life Science
(i)The living world, Cell-structure and its functions, Diversity of organism.
(ii)Bio molecules - structure and function of carbohydrates, proteins and fats, Vitamins and deficiency diseases, Enzymes, Hormones - plant hormones and growth regulation, Animal hormones and their functions.
(iii)Cell reproduction - cell cycle, Mitosis and Melosis.
(iv)Mendallion Inheritance - Monohybrid and Dihybrid cross, sex linked Inheritance, sex Determination, DNA Structure and function, DNA Replication, Protein Synthesis, Gene Regulation, Molecular basis of differentiation.
(v)Theories of Evolution of life on earth, including Human Evolution.
Group (C) Agriculture Science
(i)Different agro-climatic zones of Jharkhand, rain fall pattern and known abiotic stresses in each zone.
(ii)Ran fed agriculture: Conventional food and horticultural crops of the state, Need for diversification of crops for food as well as nutritional security in the wake of climate change; Rain water harvesting and its role in improving agriculture output in Jharkhand Fish farming.
(iii)Soil fertility status of Jharkhand Application of vermi compost and Farm. Yard Manure (FYM) for improving soil health. Nitrogen fixing bacteria; their applications and concept of Organic farming.
(iv)Concept of Agro forestry, waste lands and means to reclaim them.
(v) Government schemes for the benefit of the farmers of the state.
Group (D) Environmental Science
Concept of Ecosystem, structure and Function of Ecosystem, Natural resources Renewable and Non renewable resources, Environmental Conservation-in situ and ex situ conservation, Pollution-Air, Water, sound and soil, Solid Waste Management; Biodiversity; concept, hotspots, threats to biodiversity, Global Environmental Issues; Climate change, Global warming, Once layer depletion, Acid rain, Desertification. Environmental laws- The Environment (Protection) Act, The Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act. The Water (Prevention and control of Pollution) Act, Forest Conservation Act.
Group (E) Science and Technology Development
National Policy on Science and Technology; Energy demand of the country. Conventional and Non-conventional sources of energy. Nuclear Energy: Its merits and demerits; Trends in Nuclear Policy. NPT and CTBT. Space Technology-Indian space programmes, Application of Satellites for different purposes; Indian missile programme; Remote sensing: GIS and its application in weather forecasting disaster warning, mapping of water, soil, and mineral resources etc. Use of Biotechnology in agriculture, animal breeding, pharmaceuticals food technology and environmental conservation; possible adverse effects of biotechnological interventions; Information technology. Computers and its application in data processing, data programmes cyber crime and cyber laws.
National Health Policy : national programmes for prevention and control of Malaria, Leprosy, T.B, Cancer,Aids, Blindness etc.
परिशिष्ट - 1(ग)
|
jharkhand public service commission |
||||
|
Revised Scheme of Examination for Civil Services (Subjects) |
Duration (Hours) |
Maximum Marks |
Minimum Qualifying Marks |
Remarks |
|
(A) preliminary Examination (Screening Test) |
||||
|
General Studies-I |
2 hours |
200 |
As per the Advertisement |
Objective Type |
|
General Studies-II (Jharkhand Specific) |
2 hours |
200 |
As per the Advertisement |
Objective Type |
|
(B) Main Examination (No optional subjects. All are common compulsory papers) |
||||
|
Paper-I: General Hindi & General English, having two separate sections on (i) General Hindi and (ii) General English, each of 50 marks. |
3 hours |
100 |
As per the Advertisement |
descriptive type |
|
Paper-II: Language and Literature: Under this paper, every candidate will have to opt for one Language and Literature out of fifteen listed by the commission |
3 hours |
150 |
as above |
as above |
|
Paper-III: Social Sciences, having two distinct sections on (i) History (ii) Geography, each of equal weightage. |
3 hours |
200 |
as above |
as above |
|
Paper-IV: Indian Constitution & Polity, Public Administration & Good Governance |
3 hours |
200 |
as above |
as above |
|
Paper-V: Indian Economy, Globalization and Sustainable Development |
3 hours |
200 |
as above |
as above |
|
Paper-VI: General Sciences, Environment and Technology Development |
3 hours |
200 |
as above |
as above |
|
Total marks (Main Examination) |
- |
1050 |
Art the discretion of the commission |
- |
|
Personality Test |
- |
100 |
- |
- |
|
Grand Total |
- |
1150 |
- |
- |
Civil Services Examination (CSE) conducted by the Union Public Service Commission (UPSC) is a three-stage process –
- Preliminary Examination – Objective mode
- Mains Examination – Descriptive/written mode
- Personality Test/Interview

Through the exam, UPSC selects candidates for the various posts of All India Services (IAS, IPS and IFoS) and other Group A posts of Central Government.
UPSC Syllabus – Civil Services Preliminary Exam:
The examination notification released annually by the UPSC mentions the syllabus for all test papers in the Civil Services Examination (CSE).
The first stage of CSE is Preliminary Examination.
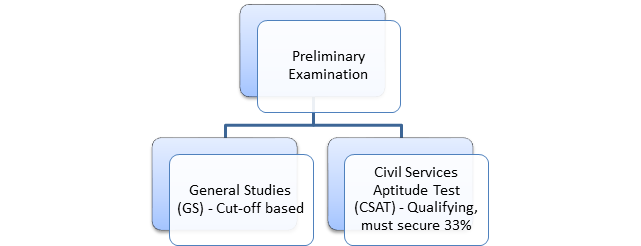
The preliminary examination or prelims (as generally called) consists of two papers – Paper I - General Studies (GS) and Paper II - Civil Services Aptitude Test (CSAT). Both these tests are of objective type i.e., Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) based questioning pattern. GS Paper consists of 100 MCQs and CSAT paper consists of 80 MCQs. Each paper is for 200 marks.
Syllabus of Paper I - GS as given by UPSC is:
- Current events of national and international importance.
- History of India and Indian National Movement.
- Indian and World Geography - Physical, Social, Economic Geography of India and the World.
- Indian Polity and Governance - Constitution, Political System, Panchayati Raj, Public Policy, Rights Issues, etc.
- Economic and Social Development Sustainable Development, Poverty, Inclusion, Demographics, Social Sector initiatives, etc.
- General issues on Environmental Ecology, Bio-diversity and Climate Change - that do not require subject specialization.
- General Science.
However, the UPSC Prelims Syllabus can be restructured as blocks of History, Geography, Polity, Economy, Ecology and Environment and General Science & Miscellaneous.
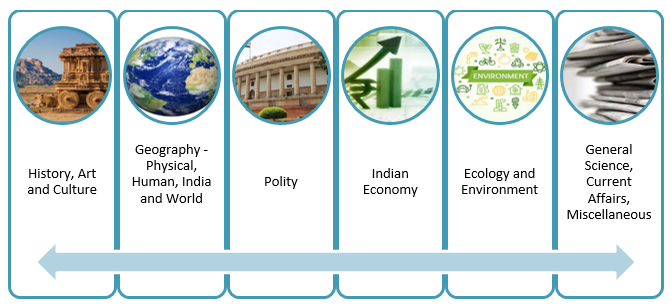
Each block can further be divided into static and dynamic portion. Aspirants are advised to first have basic knowledge and understanding of the static portions while preparing. This helps in understanding the dynamic portion with much ease.
For Example: In polity, the static part includes the existing structures of the government (at Centre, State and Local level), Parliamentary democracy, Fundamental Rights, Centre-State relations and many more. Understanding these will help aspirants in tackling any dynamic portion be it issues like Kaveri river dispute, Khap panchayat, right to marry beyond religion, electoral reforms etc.
Lastly, aspirants must look at the events from various angles. One must be able to appreciate the fact that all things are related to each other.
Syllabus of Paper II - CSAT:
CSAT is an aptitude test. In this, an aspirant must secure a minimum of 33% marks to qualify for the written examination. The paper is qualifying in nature.
The syllabus includes –
- Comprehension
- Interpersonal skills including communication skills
- Logical reasoning and analytical ability
- Decision-making and problem-solving
- General mental ability
- Basic numeracy (numbers and their relations, orders of magnitude, etc.) (Class X level), Data
- interpretation (charts, graphs, tables, data sufficiency etc. - Class X level)
- English Language Comprehension skills (Class X level).
Note: UPSC has clearly mentioned in the notification that the English Language Comprehension Skills (Class X Level) to be tested will be entirely of English language without Hindi translation.
UPSC Syllabus – Civil Services Mains Exam:
Pattern:
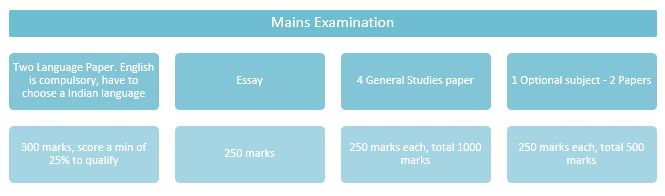
Marks scored in Essay, General studies and optional subject are considered for preparation of merit list.
UPSC Mains Syllabus:
Essay:
Candidates will be required to write an essay on a specific topic. The choice of subjects will be given. They will be expected to keep closely to the subject of the essay to arrange their ideas in orderly fashion, and to write concisely. Credit will be given for effective and exact expression.
General Studies-I (Indian Heritage and Culture, History and Geography of the World and Society) of 250 marks which may include following topics:
- Indian culture will cover the salient aspects of Art Forms, Literature and Architecture from ancient to modern times.
- Modern Indian history from about the middle of the eighteenth century until the present - significant events, personalities, issues
- The Freedom Struggle - its various stages and important contributors /contributions from different parts of the country.
- Post-independence consolidation and reorganization within the country. History of the world will include events from 18th century such as industrial revolution, world wars, redrawal of national boundaries, colonization, decolonization, political philosophies like communism, capitalism, socialism etc.- their forms and effect on the society.
- Salient features of Indian Society, Diversity of India.
- Role of women and women's organization, population and associated issues, poverty and developmental issues, urbanization, their problems and their remedies.
- Effects of globalization on Indian society
- Social empowerment, communalism, regionalism & secularism.
- Salient features of world's physical geography.
- Distribution of key natural resources across the world (including South Asia and the Indian subcontinent); factors responsible for the location of primary, secondary, and tertiary sector industries in various parts of the world (including India)
- Important Geophysical phenomena such as earthquakes, Tsunami, Volcanic activity, cyclone etc., geographical features and their location- changes in critical geographical features (including water bodies and ice-caps) and in flora and fauna and the effects of such changes.
General Studies -II (Governance, Constitution, Polity, Social Justice and International relations) of 250 marks which may include following topics:
- Indian Constitution- historical underpinnings, evolution, features, amendments, significant provisions and basic structure.
- Functions and responsibilities of the Union and the States, issues and challenges pertaining to the federal structure, devolution of powers and finances up to local levels and challenges therein.
- Separation of powers between various organs dispute redressal mechanisms and institutions.
- Comparison of the Indian constitutional scheme with that of other countries
- Parliament and State Legislatures - structure, functioning, conduct of business, powers & privileges and issues arising out of these.
- Structure, organization and functioning of the Executive and the Judiciary Ministries and Departments of the Government; pressure groups and formal/informal associations and their role in the Polity.
- Salient features of the Representation of People's Act.
- Appointment to various Constitutional posts, powers, functions and responsibilities of various Constitutional Bodies.
- Statutory, regulatory and various quasi-judicial bodies
- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
- Development processes and the development industry- the role of NGOs, SHGs, various groups and associations, donors, charities, institutional and other stakeholders
- Welfare schemes for vulnerable sections of the population by the Centre and States and the performance of these schemes; mechanisms, laws, institutions and Bodies constituted for the protection and betterment of these vulnerable sections.
- Issues relating to development and management of Social Sector/Services relating to Health, Education, Human Resources.
- Issues relating to poverty and hunger.
- Important aspects of governance, transparency and accountability, e-governance- applications, models, successes, limitations, and potential; citizens charters, transparency & accountability and institutional and other measures.
- Role of civil services in a democracy.
- India and its neighborhood- relations.
- Bilateral, regional and global groupings and agreements involving India and/or affecting India's interests
- Effect of policies and politics of developed and developing countries on India's interests, Indian diaspora. Important International institutions, agencies and fora- their structure, mandate.
General Studies -III (Technology, Economic Development, Bio-diversity, Environment, Security and Disaster Management) of 250 marks which may include following topics:
- Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization of resources, growth, development and employment.
- Inclusive growth and issues arising from it.
- Government Budgeting.
- Major crops cropping patterns in various parts of the country, different types of irrigation and irrigation systems storage, transport and marketing of agricultural produce and issues and related constraints; e-technology in the aid of farmers
- Issues related to direct and indirect farm subsidies and minimum support prices; Public Distribution System- objectives, functioning, limitations, revamping; issues of buffer stocks and food security; Technology missions; economics of animal-rearing.
- Food processing and related industries in India- scope and significance, location, upstream and downstream requirements, supply chain management.
- Land reforms in India.
- Effects of liberalization on the economy, changes in industrial policy and their effects on industrial growth.
- Infrastructure: Energy, Ports, Roads, Airports, Railways etc.
- Investment models.
- Science and Technology- developments and their applications and effects in everyday life
- Achievements of Indians in science & technology; indigenization of technology and developing new technology.
- Awareness in the fields of IT, Space, Computers, robotics, nano-technology, bio-technology and issues relating to intellectual property rights.
- Conservation, environmental pollution and degradation, environmental impact assessment
- Disaster and disaster management.
- Linkages between development and spread of extremism
- Role of external state and non-state actors in creating challenges to internal security
- Challenges to internal security through communication networks, role of media and social networking sites in internal security challenges, basics of cyber security; money-laundering and its prevention
- Security challenges and their management in border areas; linkages of organized crime with terrorism
- Various Security forces and agencies and their mandate
General Studies -IV (Ethics, Integrity and Aptitude) of 250 marks which may include following topics:
This paper will include questions to test the candidates' attitude and approach to issues relating to integrity, probity in public life and his problem-solving approach to various issues and conflicts faced by him in dealing with society. Questions may utilize the case study approach to determine these aspects. The following broad areas will be covered.
- Ethics and Human Interface: Essence, determinants and consequences of Ethics in human actions; dimensions of ethics; ethics in private and public relationships. Human Values - lessons from the lives and teachings of great leaders, reformers and administrators; role of family, society and educational institutions in inculcating values.
- Attitude: content, structure, function; its influence and relation with thought and behaviour; moral and political attitudes; social influence and persuasion. Aptitude and foundational values for Civil Services, integrity, impartiality and non-partisanship, objectivity, dedication to public service, empathy, tolerance and compassion towards the weaker sections.
- Emotional intelligence-concepts, and their utilities and application in administration and governance.
- Contributions of moral thinkers and philosophers from India and world.
- Public/Civil service values and Ethics in Public administration: Status and problems; ethical concerns and dilemmas in government and private institutions; laws, rules, regulations and conscience as sources of ethical guidance; accountability and ethical governance; strengthening of ethical and moral values in governance; ethical issues in international relations and funding; corporate governance.
- Probity in Governance: Concept of public service; Philosophical basis of governance and probity; Information sharing and transparency in government, Right to Information, Codes of Ethics, Codes of Conduct, Citizen's Charters, Work culture, Quality of service delivery, Utilization of public funds, challenges of corruption.
- Case Studies on above issues
Optional Subject Papers I & II
List of optional subjects for Main Examination:
Agriculture; Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Science; Anthropology; Botany; Chemistry; Civil Engineering; Commerce and Accountancy; Economics; Electrical Engineering; Geography; Geology; History; Law; Management; Mathematics; Mechanical Engineering; Medical Science; Philosophy; Physics ; Political Science and International Relations; Psychology; Public Administration; Sociology; Statistics; and Zoology.
Literature of any one of the following languages:
Assamese, Bengali, Bodo, Dogri, Gujarati, Hindi, Kannada, Kashmiri, Konkani, Maithili, Malayalam, Manipuri, Marathi, Nepali, Oriya, Punjabi, Sanskrit, Santhali, Sindhi, Tamil, Telugu, Urdu, English.
Candidates may choose any optional subject from the list of subjects given above.
UPSC Syllabus – Civil Services Interview:
According to the UPSC, the test is intended to judge the mental calibre of a candidate. In broad terms, this is really an assessment of not only her/his intellectual qualities but also social traits and her/his interest in current affairs. Some of the qualities to be judged are mental alertness, critical powers of assimilation, clear and logical exposition, balance of judgement, variety and depth of interest, ability for social cohesion and leadership, intellectual and moral integrity.



